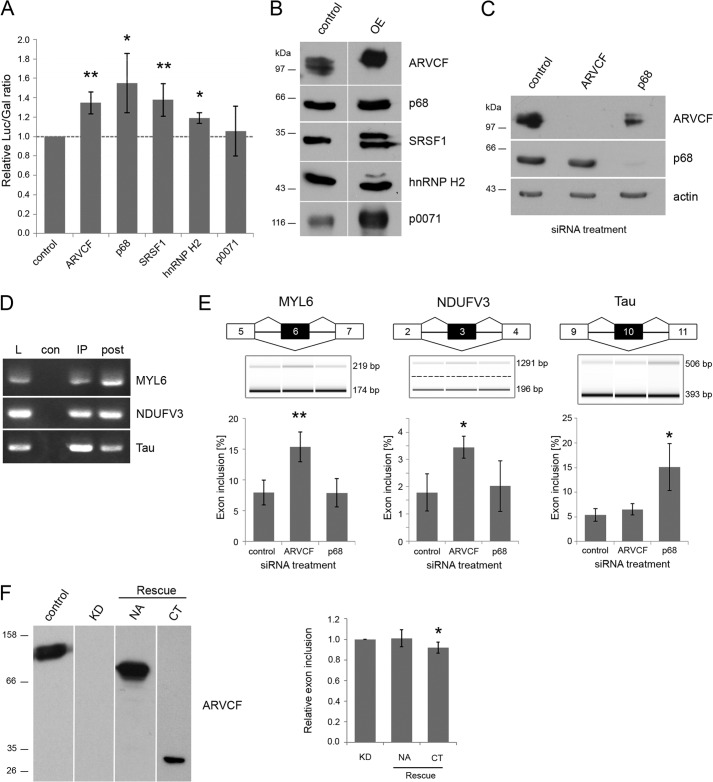
FIGURE 7.
ARVCF regulates pre-mRNA splicing. A, double reporter splicing assay in HEK 293 cells co-transfected with the reporter plasmid pTN23 and the cDNAs coding for ARVCF, p68, SRSF1, hnRNP H2, p0071, or empty vector as control. The ratio of luciferase to β-galactosidase activity is shown. B and C, verification of protein overexpression and knockdown via Western blot analysis. Laemmli lysates of HEK 293 cells transfected with the plasmids (B) or siRNAs (C) indicated at the top were separated on SDS gels and analyzed via Western blot with the antibodies indicated on the right. Equal amounts of lysates were loaded, except for ARVCF overexpression less lysate was used. OE, overexpressing HEK 293 cells. D, samples from RNA immunoprecipitations of ARVCF were analyzed by RT-PCR with primers against MYL6, NDUFV3, and Tau. E, capillary gel electrophoresis of RT-PCR products from HEK 293 cells treated with siRNA as indicated. Primers against the targets MYL6, NDUFV3, and Tau are used. The percentage of exon inclusion for these gene products is calculated. F, mARVCF constructs containing the N-terminal and Arm repeat domain (NA) or the C-terminal domain (CT) only were expressed in siRNA-treated HEK 293 cells verified by Western blotting using antibodies, as indicated. The percentage of exon inclusion for MYL6 was measured and normalized to siRNA-treated cells transfected with empty vector (KD). n ≥ 3 biological replicates. Error bars, S.D.; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.