FIGURE 2.
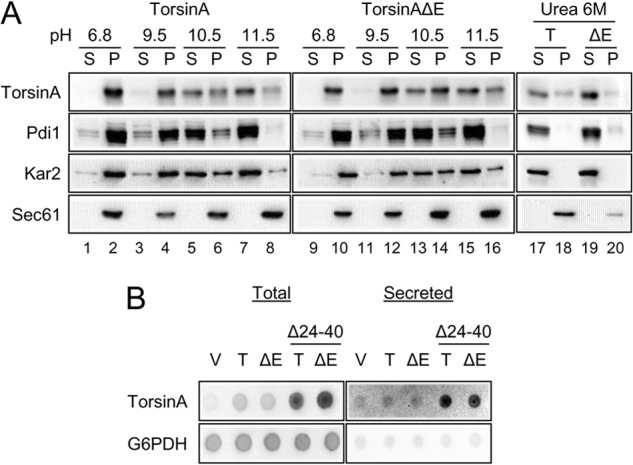
TorsinA and torsinAΔE peripherally associate with the yeast ER membrane through an N-terminal hydrophobic domain. A, ER-derived microsomes were prepared from log phase wild-type yeast cells grown at 28 °C that expressed torsinA or torsinAΔE and were incubated in a pH 6.8 buffer, in 25 mm CHES, pH 9.5 buffer, 25 mm CAPS, pH 10.5 buffer, 0.1 m Na2CO3, pH ∼11.5, or in 6 m urea for 30 min in ice. After centrifugation at 100,000 × g, aliquots from the supernatant (S) or the pellet (P) fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE, and the presence of torsinA and torsinAΔE was detected by Western blot. Pdi1 is a lumenal ER protein; Kar2 is a peripherally associated ER lumenal protein, and Sec61 is an integral membrane ER protein. B, nitrocellulose membranes spotted with overnight yeast cultures transformed with vector alone (V) or expressing torsinA (T) or torsinAΔE (ΔE), were layered on top of solid selective medium and incubated for ∼20 h at 30 °C. To detect secreted proteins, cells were washed off the nitrocellulose membrane with water. To detect total protein (intracellular and secreted material), cells were lysed in situ and then washed. TorsinA and G6PDH were detected by Western (“dot”) blot. Please note that secreted proteins yield a higher signal than their nonsecreted counterparts in the total protein blot (82).
