FIGURE 4.
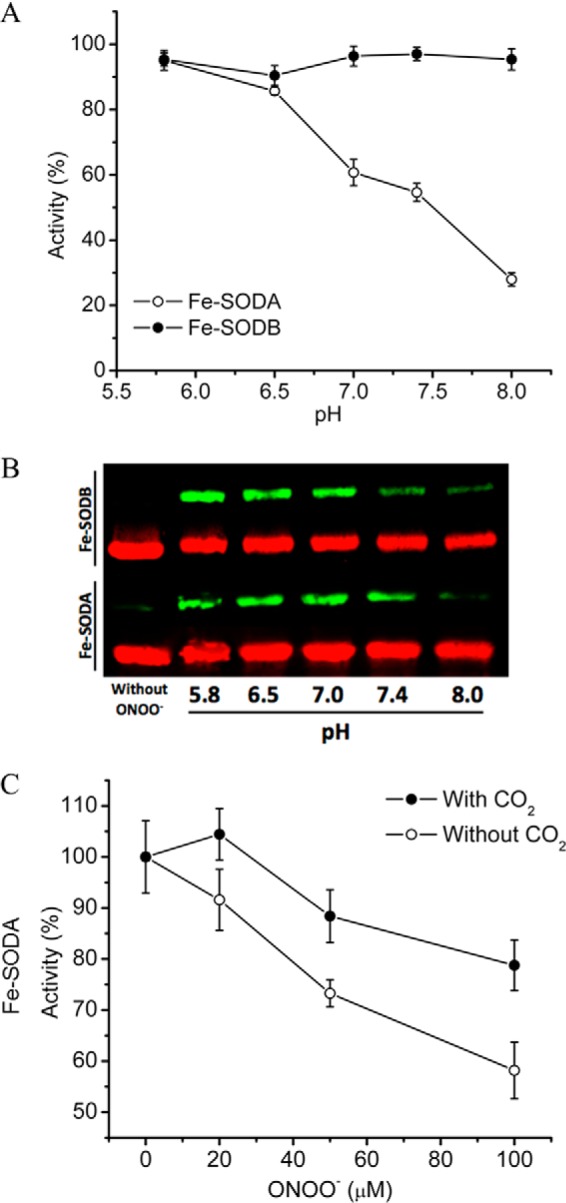
Effects of pH and CO2 on the peroxynitrite-dependent inactivation of T. cruzi Fe-SODs. A, pH-dependent peroxynitrite-mediated inactivation. Peroxynitrite (150 μm) was added to Fe-SODA (empty circles) and Fe-SODB (filled circles) (8 μm) in sodium phosphate buffer (100 mm) at different pH values (5.5–8.0), and residual Fe-SOD activity was measured. Activity is expressed relative to the native enzyme incubated in the absence of peroxynitrite (100% activity) at the indicated pH values. B, pH-dependent peroxynitrite-mediated nitration. Immunochemical detection of 3-nitrotyrosine was performed after peroxynitrite (150 μm) exposure to either Fe-SODA or Fe-SODB (8 μm) in sodium phosphate buffer (100 mm) at different pH values using specific anti-NO2-Tyr antibodies (green). Equal loading of T. cruzi Fe-SOD samples were evaluated by specific Fe-SODA and Fe-SODB antibodies (red). C, effect of CO2 in the peroxynitrite reaction with Fe-SODA. Peroxynitrite (0–100 μm) was added to Fe-SODA (8 μm) in sodium phosphate buffer 100 mm, pH 7.4, in the presence (filled circles) or absence (empty circles) of bicarbonate (24 mm; CO2 = 1.3 mm)), and residual SOD activity was measured. Activity is expressed relative to the non-treated enzyme in the presence or absence of bicarbonate. Error bars, S.E.
