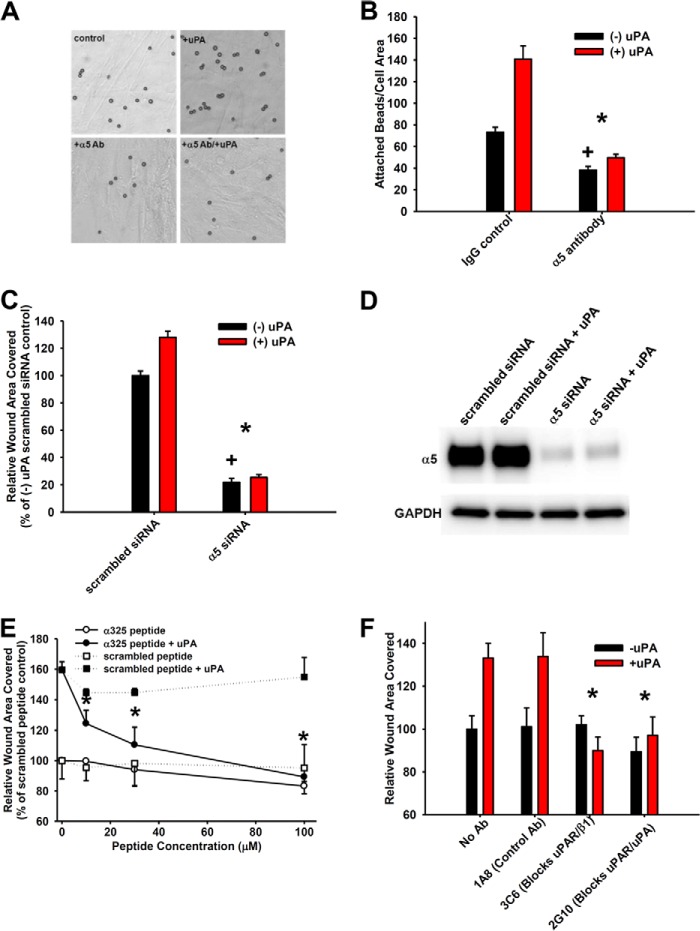
FIGURE 3.
Integrin α5β1-uPAR interactions are required for uPAR ligation-induced integrin function and motility. A and B, FN-coated beads were applied to fibroblasts that were pretreated with or without ATF (10 nm, 30 min) and with or without α5 function-blocking antibody (α5 Ab, 10 μg/ml), and the number of beads/cell area was counted. A–D, *, p < 0.05 denotes loss of uPA-induced attachment or hypermotility versus increase under control conditions (IgG, scrambled siRNA). +, p < 0.05 denotes comparison among basal (−uPA) conditions. A, representative photomicrographs. B, quantification of bead attachment. C, fibroblast monolayer migration with or without α5 or scrambled siRNA with or without ATF (10 nm). D, validation of α5 siRNA knockdown by Western blot. E, fibroblast monolayer migration with or without α325 or scrambled peptide with or without 10 nm ATF. Conditions were as indicated. *, p < 0.05 denotes loss of uPA-induced hypermotility with α325 peptide compared with scrambled peptide under +uPA (10 nm ATF) conditions. F, fibroblast monolayer migration with or without antibodies (10 μg/ml each) 1A8 (control antibody), 3C6 (which blocks uPAR-β1 interactions), or 2G10 (which blocks uPAR-uPA interactions) with or without 10 nm ATF. *, p < 0.05 denotes loss of uPA-induced hypermotility with 3C6 or 2G10 antibody versus 1A8 under +uPA (10 nm ATF) conditions. Error bars, S.E.