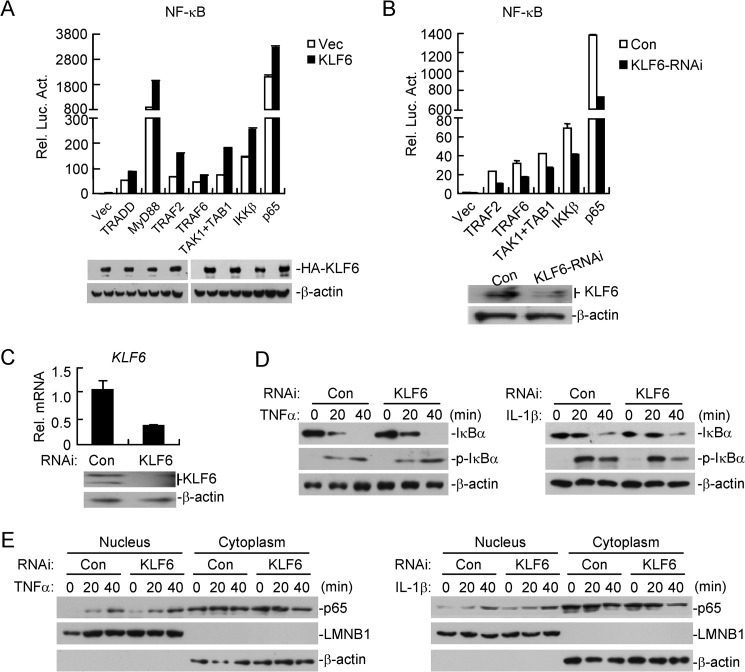
FIGURE 3.
KLF6 is dispensable for TNFα- and IL-1β-triggered nuclear translocation of NF-κB. A, overexpression of KLF6 potentiates TRADD-, MyD88-, TRAF2-, TRAF6-, TAK1/TAB1-, IKKβ-, or p65-mediated NF-κB activation. HEK293 cells (1 × 105) were transfected with an empty control vector or HA-tagged KLF6 expression plasmid (0.05 μg) and the indicated plasmids (0.1 μg each). Reporter assays were performed 20 h after transfection. The lysates were analyzed by immunoblots with anti-HA or anti-β-actin. B, knockdown of KLF6 inhibits TAK1/TAB1-, TRAF2-, TRAF6-, IKKβ-, or p65-mediated NF-κB activation. KLF6-RNAi or control cell line, which was constructed in 293 cells (1 × 105) was transfected with the indicated plasmids (0.1 μg each) and NF-κB reporter plasmid (0.02 μg). Reporter assays were performed 20 h after transfection. The efficiency of the knockdown of KLF6 was analyzed by immunoblots. C, construction of a KLF6-RNAi stable cell line. HCT116 cells were stably transfected with control RNAi or KLF6-RNAi by retroviral-mediated gene transfer. The cells (4 × 105) were analyzed by qPCR or immunoblots. D, knockdown of KLF6 has no marked effects on TNFα- or IL-1β-triggered phosphorylation and degradation of IκBα. The cells in C (2 × 105) were treated with TNFα (20 ng/ml) or IL-1β (10 ng/ml) for the indicated time points before immunoblot analysis was performed. E, knockdown of KLF6 has no marked effects on p65 translocation. Cells in C (2 × 105) were treated with TNFα (20 ng/ml) or IL-1β (10 ng/ml) for the indicated time points. The cytoplasm extracts were prepared in 1 ml of homogenization buffer, whereas the nuclear extracts were prepared in 0.2 ml of nuclear lysis buffer. Equal volumes of the cytoplasm and nuclear extracts were loaded for immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies.