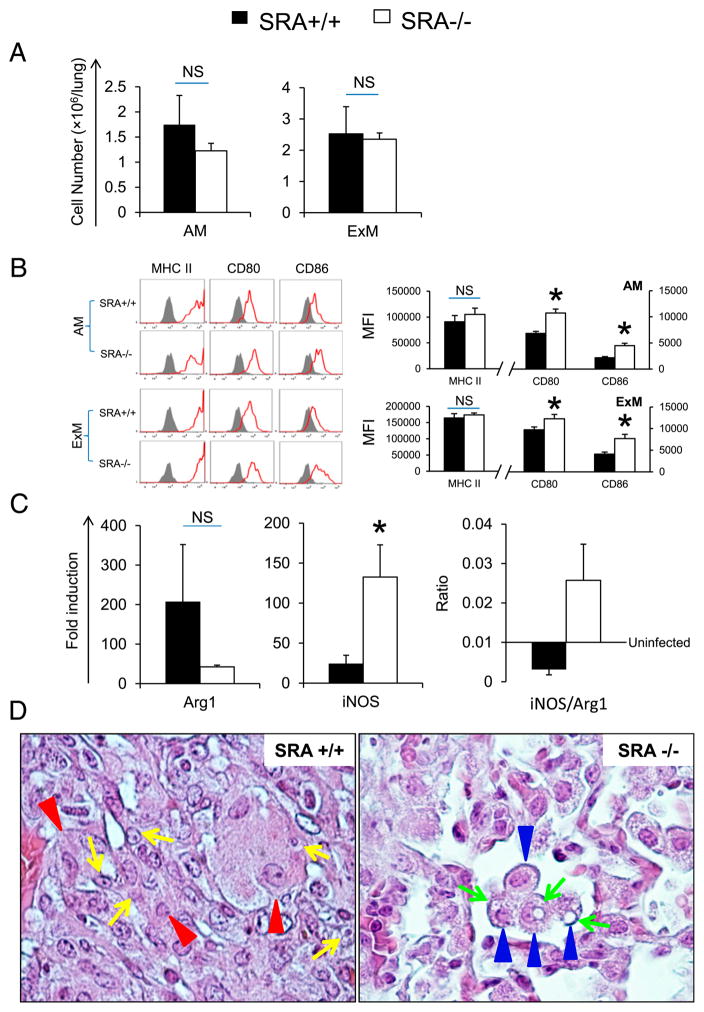
FIGURE 5.
Effect of SRA on the activation of pulmonary macrophages. Pulmonary macrophages including AMs and ExMs were isolated from infected SRA+/+ and SRA−/− mice at 3 wpi using flow cytometry as per Materials and Methods. In brief, total macrophages (autofluorescence+/CD11c+) were gated as described in Fig. 3. Next, AMs (CD11c+/CD11blow) and ExMs (CD11c+/CD11bhigh) were identified based on the expression of CD11c versus CD11b. Total numbers of AMs and ExMs were determined by multiplying the frequency of each subset by the total number of CD45+ leukocytes (A). Thereafter, the activation phenotype of AM and ExM was evaluated by the surface expression of MHC class II and costimulatory molecules (CD80 and CD86). Stained samples are shown as solid lines and isotype controls as shaded histograms. The bar graph presents mean frequencies of positive cells derived from these histograms (B). Gene expression of alternative macrophage activation (Arg1) and classical macrophage activation (iNOS) by total adherent pulmonary macrophages was evaluated by qPCR (as described in Materials and Methods) (C). Data were pooled from two to three separate matched experiments; n ≥ 6 for each of the analyzed parameters. *p <0.05 in comparison between SRA+/+ mice and SRA−/− mice. NS, No significant difference between SRA+/+ mice and SRA−/− mice. The morphologic appearance of pulmonary macrophages was evaluated (at 3 wpi by histology as described in Fig. 2). (D) Representative photomicrographs of H&E and mucicarmine-stained slides taken at 100× objective power. Note that the macrophages identified within infected lungs of SRA+/+ mice (red arrowheads) were large, sometimes multinu-cleated, and frequently contained intact intracellular cryptococci (yellow arrows). In contrast, macrophages (blue arrows) in the lungs of SRA−/− mice appeared smaller and often harbored degraded cryptococci (green arrows).