Figure 1.
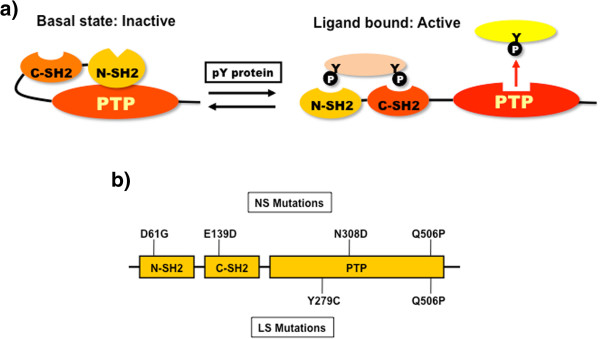
SHP2 regulation and disease-associated mutants. a) SHP2 is regulated via a “self-locking” mechanism: in the absence of pTyr- proteins (pY), SHP2 exists in a closed conformation with the N-SH2 domain bound to the PTP domain, blocking the catalytic site. Upon binding of the appropriate pTyr-proteins, the closed confirmation is disrupted, opening up SHP2 so that substrates can bind to the active site. b) Positions of human disease-associated mutants used in this study.
