Figure 3.
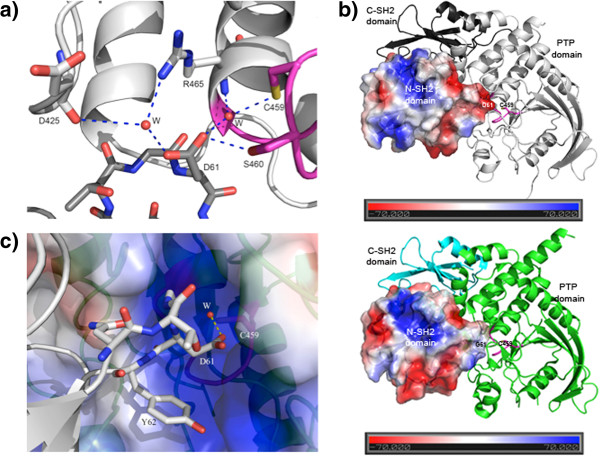
Crystal structure of the D61G mutant. a) In WT SHP2, the side chain of Asp61 (in the N-SH2 domain) forms a direct hydrogen bond with Ser460, a water-mediated hydrogen bond with the catalytic cysteinyl residue Cys459 and two water-mediated hydrogen bonds with Arg465 in the PTP domain. b) The D61G mutation alters the electrostatic surface charge on the N-SH2 domain along its interaction interface with the PTP domain catalytic pocket. The N-SH2 domain is rendered in electrostatic surface representation, the C-SH2 domain is colored dark grey (WT structure; top panel) or cyan (D61G mutant structure; bottom panel), and the PTP domain is shown in grey (WT) or green (D61G). The catalytic P-loop (458–464) is shown in magenta. c) The N-SH2/PTP domain interface near the catalytic site. The PTP domain is rendered in electrostatic surface presentation, and shows a mostly positively charged catalytic site opposite to Asp61. A conserved water molecule mediates a hydrogen bond between Asp61 and Cys459.
