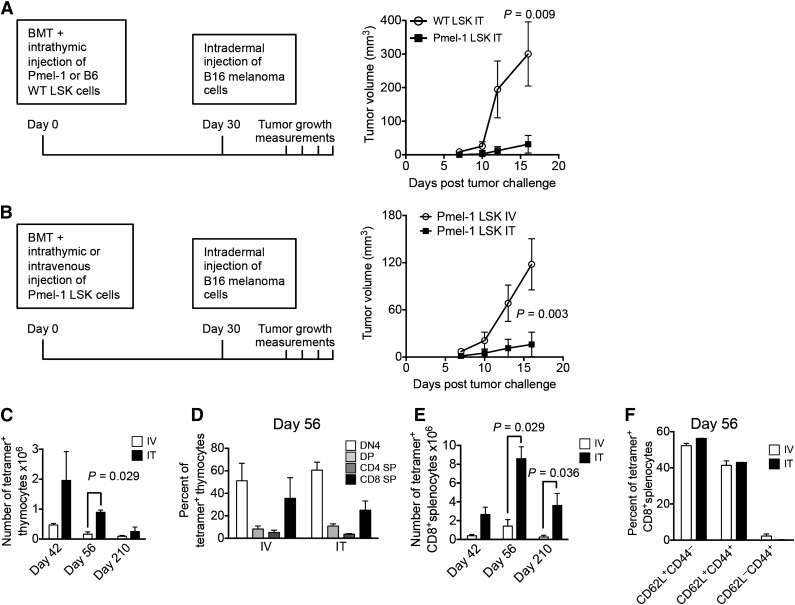
Figure 6.
ITI of HSPCs from Pmel-1 mice inhibits intradermal growth of melanoma cells. (A) Lethally irradiated C57BL/6 recipients were transplanted with C57BL/6 Lin− BM cells and received 10 000 C57BL/6.Pmel-1 or WT C57BL/6 LSK cells via ITI 2 hours after irradiation. B16 melanoma cells were injected intradermally on day 30 after BMT and tumor volumes were measured manually at days 7, 10, 12, and 16. Mean and SEM are presented (n = 5-6). (B) Lethally irradiated C57BL/6 recipients were transplanted with C57BL/6 TCD BM cells and received 10 000 C57BL/6.Pmel-1 LSK cells intravenously or via ITI 2 hours after irradiation. B16 melanoma cells were injected intradermally on day 30 after BMT and the tumor volume was measured manually at days 7, 10, 13, and 16. Mean and SEM of 1 of 2 independent experiments are presented (n = 8). (C) Animals were transplanted as described in panel B but did not receive tumor cell injections. Thymuses were harvested on days 42, 56, and 210 after BMT and analyzed for tetramer-positive total thymocyte numbers. Mean and SEM of 2 independent experiments are presented (n = 4). (D) Animals were transplanted as described in panel C. Thymuses were harvested on day 56 after BMT and analyzed for tetramer-positive thymocyte subsets. Mean and SEM of 2 independent experiments are presented (n = 4). (E) Animals were transplanted as described in panel C. Spleens were harvested on days 42, 56, and 210 after BMT and analyzed for tetramer-positive CD8+ T cells. Mean and SEM of 2 independent experiments are presented (n = 4). (F) Animals were transplanted as described in panel C. Spleens were harvested on day 56 after BMT and analyzed for tetramer-positive CD8+ T-cell subsets. Mean and SEM of 2 independent experiments are presented (n = 4). IT, intrathymic; IV, intravenous.