Figure 2.
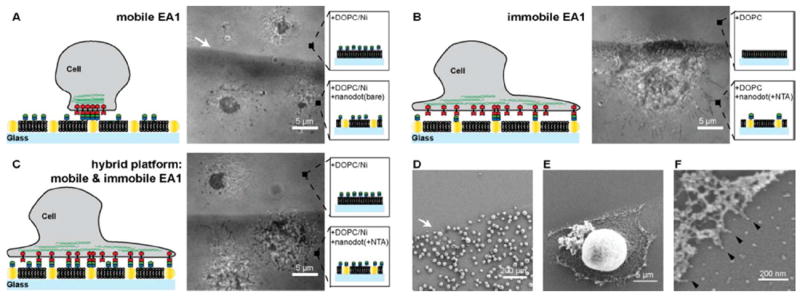
MDA-MB-231 cells are placed on substrates with different ephrin-A1 presentations. A) RICM image of MDA-MB-231 cells placed on a mobile ephrin-A1 surface is shown. Cells form a tight contact area with the SLB displaying mobile ephrin-A1 on both the nanodot patterned side as well as the glass side. B) RICM image of cells placed on immobile ephrin-A1 surface shows a spreading morphology and filopodia protrusions. Essentially no cells attached to a pure 100% DOPC SLB. C) RICM image of cells on hybrid surfaces, consisting of both mobile and immobile ephrin-A1. Cells on the bare glass side that displays only mobile ephrin-A1 form the typical central contact region whereas cells on the hybrid nanodot side spread out, forming protrusions, similar to cells on the immobile ephrin-A1 surface. D-F) SEM images of MDA-MB-231 cells on the immobile ephrin-A1 substrate. Cells are preferentially interacting with the nanodot side since the phospholipids are not functionalized with ephrin-A1. Higher magnification SEM images reveal that individual cell protrusions are interacting with single nanodots (black arrows).
