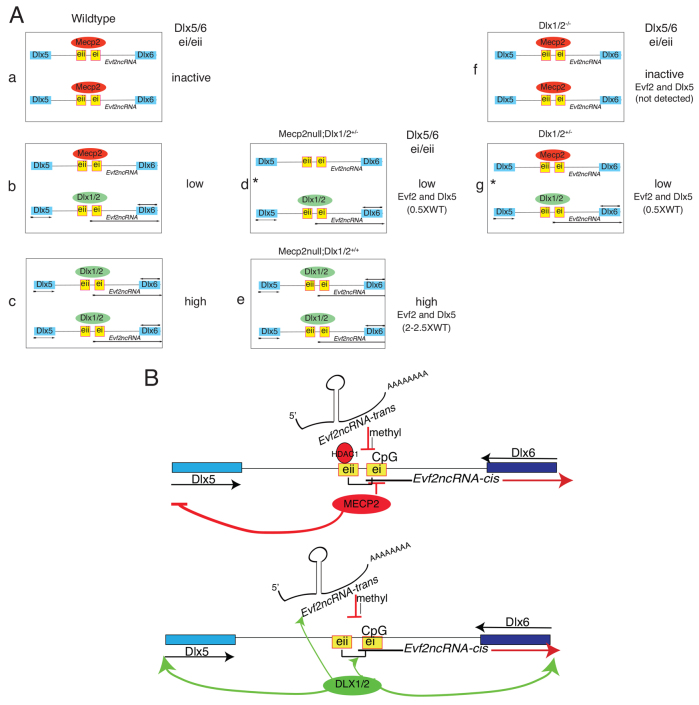
Fig. 6.
Models describing Mecp2, Dlx1/2 and Dlx5/6 enhancer interactions. (A) Model describing the relationship between Mecp2 and Dlx1/2 occupancy of Dlx5/6ei and eii enhancers and transcriptional activity (see Discussion for details). (B) Model describing how the Evf2 lncRNA facilitates differential dosage control of adjacent genes regulated by common enhancer elements. Evf2 lncRNA inhibits enhancer methylation and mediates recruitment of transcriptional repressor and activator. Schematic summarizes the relationship between enhancer methylation, Evf2 lncRNA trans- and cis-effects, and antagonism between recruited transcription factors DLX1/2 and MECP2. Genetic epistasis experiments support the hypothesis that binding of MECP2 occurs in competition with DLX1/2 at Dlx5/6ei and eii, rather than cooperatively. Removal of one copy of DLX1/2 from MECP2 null mice decreases levels of Evf2 and Dlx5, supporting antagonism between MECP2 and DLX1/2. Whereas MECP2 represses Dlx5 and Evf2, DLX1/2 activates Dlx5, Dlx6 and Evf2 expression. DLX1/2 increases Evf2 expression, which inhibits 576CpG and 757CpG site-specific methylation of Dlx5/6ei in trans.