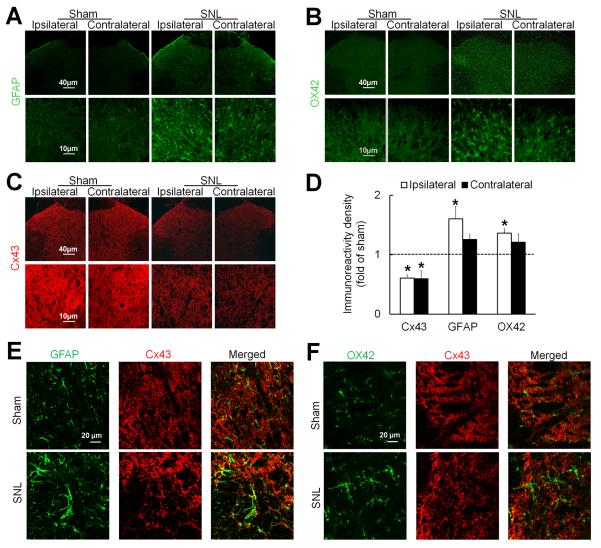
Fig. 2. Spinal nerve injury increases glial activation but decreases Cx43 immunoreactivity in the spinal cord.
(A) In rats on day 14 after spinal nerve ligation (SNL), astrocytes in the spinal cord exhibited increased immunoreactivity of GFAP, especially on the side ipsilateral (left) to nerve injury. (B) Meanwhile, microglia exhibited increased immunoreactivity of OX42. Compared to spinal astrocytes and microglia in sham-operated rats, those in SNL rats were hypertrophic. (C) In contrast, Cx43 immunoreactivity was decreased on both sides of the spinal cord in SNL rats compared to that in sham-operated rats. (D) Quantification of Cx43, GFAP, and OX42 immunoreactivity in the ipsilateral and contralateral dorsal horn. The immunostaining density of SNL rats (3–4 sections/rat, n=3) were normalized to that of sham-operated rats (n=3). *P < 0.05 versus sham-operated rats, student t-test. Data are expressed as mean+ SEM. (E) The overlap (yellow) of GFAP (green) and Cx43 (red) immunoreactivity was increased after SNL. (F) OX42 (green) and Cx43 (red) did not colocalize.