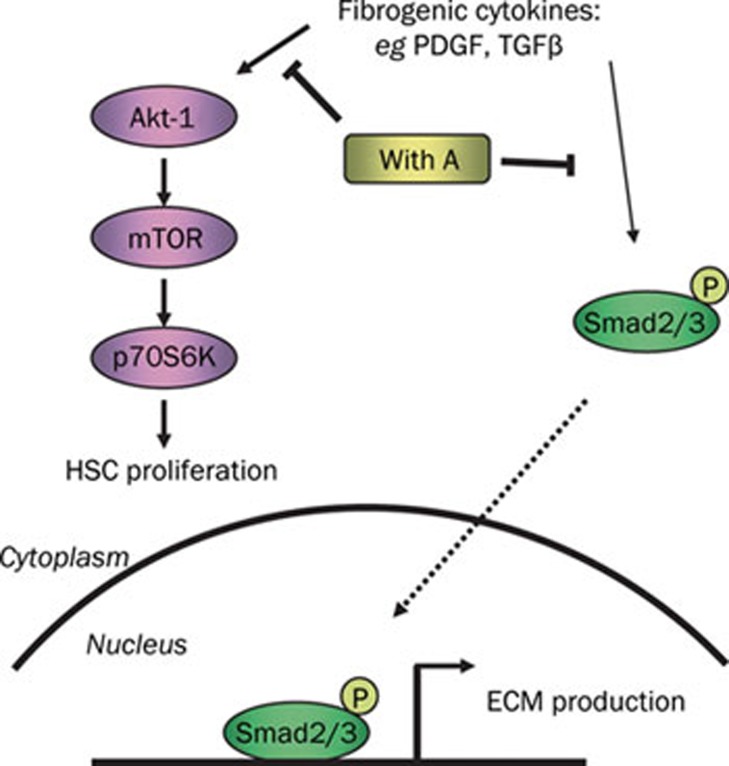
Figure 6.
Proposed model illustrating the anti-fibrotic mechanism of Withagulatin A (With A). During liver fibrosis, stimulatory signals from the fibrogenic cytokines including PDGF and TGF-β are transduced into target cells through their corresponding receptors, which in turn activate Akt and Smad proteins by phosphorylation. Withagulatin A inhibited the phosphorylation of Akt and its downstream targets such as mTOR and p70S6K, which finally led to reduced HSC proliferation. Meanwhile, Withagulatin A suppressed Smad2/3 phosphorylation and consequently blocked translocation to the nucleus, thereby resulting in reduced transcription of ECM proteins.