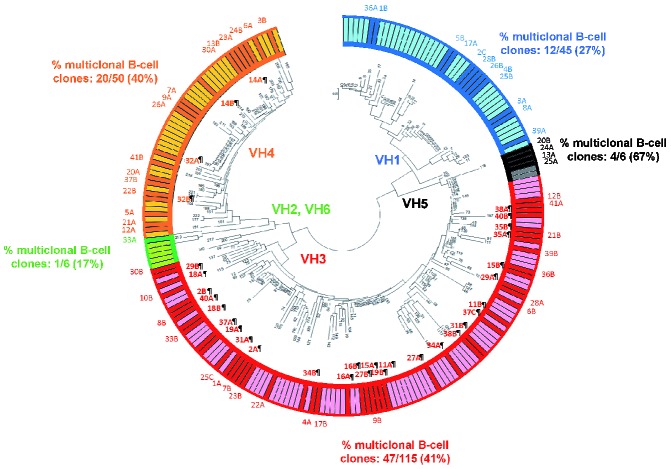
Figure 2.
Sequence distance cladogram of IGHV gene usage in CLL-like and non-CLL-like B-cell clones from multiclonal (dark colored bars in the outside circle) and monoclonal (light colored bars in the outside circle) cases. Five major branches were found in the sequence distance cladogram (i.e VH1, VH5, VH3, VH2-VH6, VH4). B-cell clones from individual multiclonal cases are represented by numbers; from them, those phylogenetically closely related B-cell clones, which share the same IGHV family, are specifically identified by bold numbers in the inner part of the circle and the symbol ¶. Of note, B-cell clones from multiclonal cases 14¶, 16¶ and 35¶ belong to closely located sub-branches of the cladogram, with their IGHV sequences having amino acid identity of 79%, 76% and 69%, respectively. In turn, B-cell clones from the multiclonal case 32¶ belong to the VH4 major branch with IGHV sequences whose amino acid identity is 69%. Finally, the other B-cell clones from multiclonal cases – cases 2¶, 11¶, 15¶, 18¶, 19¶, 27¶, 29¶, 31¶, 34¶, 37¶, 38¶ and 40¶– belong to the VH3 major branch, having IGHV sequences with amino acid identity > 60% (68%, 73%, 73.4%, 61%, 79%, 70%, 63%, 77%, 69.9%, 70%, 72% and 68.4%, respectively).