Figure 1.
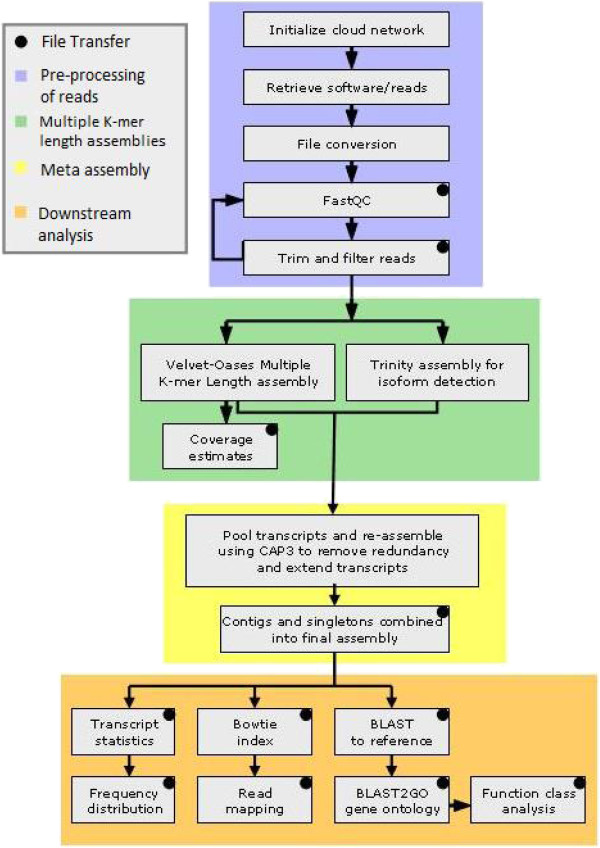
Flowchart of the bioinformatic pipeline. The pipeline performs multiple operations from sequence editing to annotation. First, a cloud network is initialized and algorithms are retrieved and installed. The sequence reads are parsed and filtered for quality and removal of adaptor sequences (blue). Next, assemblies are generated using various k-mer lengths and algorithms to create a diversity of transcript fragments (green). Then, the transcripts from all assemblies are pooled and re-assembled to remove redundant contigs and extend sequences based on overlap (yellow). The resulting multiple k-mer length meta-assembly is then analyzed and formatted for various downstream applications. Reads are mapped back to contigs, genes are annotated, and gene ontology is applied using BLAST and Blast2GO (orange). The pipeline generates an analysis of the assembly and the quantity and distribution of sequences. The resulting data is packaged in an archive for transfer and the cloud network is disbanded.
