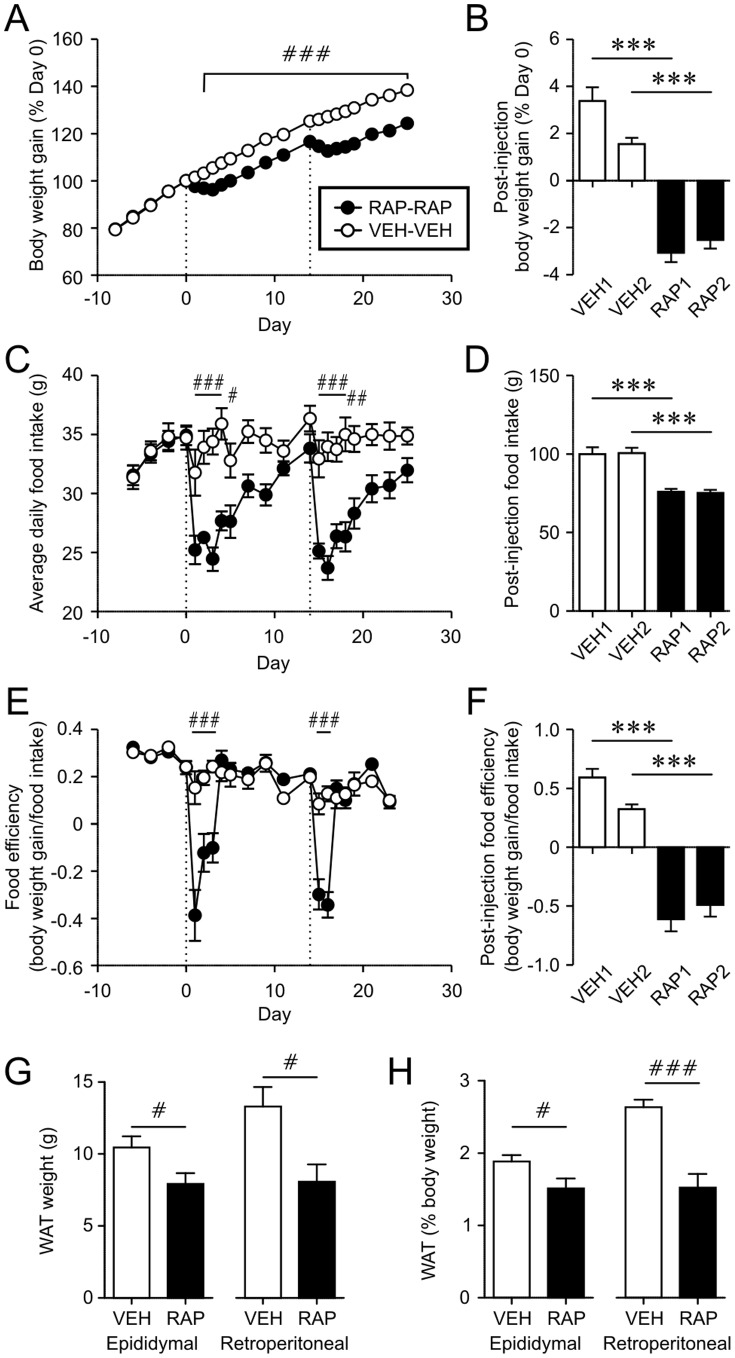
Figure 2. Spaced injections of rapamycin have additive effect on body weight gain.
A–C: A, C and E: Body weight gain (A), daily food intake (C) and food efficiency (E) of rats given two i.p. injections (broken lines, Day 0 and 14) of RAP (10 mg/kg each) or VEH with a 2-week interval. # p<0.05, ## p<0.01, ### p<0.001, VEH vs. RAP (two-way Mixed-ANOVA). Horizontal bars indicate the days when significance was seen. B, D and F: Cumulative body weight gain, food intake and food efficiency during the first three days post-injection. ***p<0.001, VEH vs. RAP. There was no statistical difference between two injections within the group (VEH1 vs. VEH2, RAP1 vs. RAP2) (two-way Mixed-ANOVA). G: The weight of white adipose tissues (WAT), epididymal and retroperitoneal pads, in rats treated twice with VEH or RAP. H: WAT weight normalized to the body weight of individual rat. # p<0.05, ### p<0.001 (unpaired t-test).