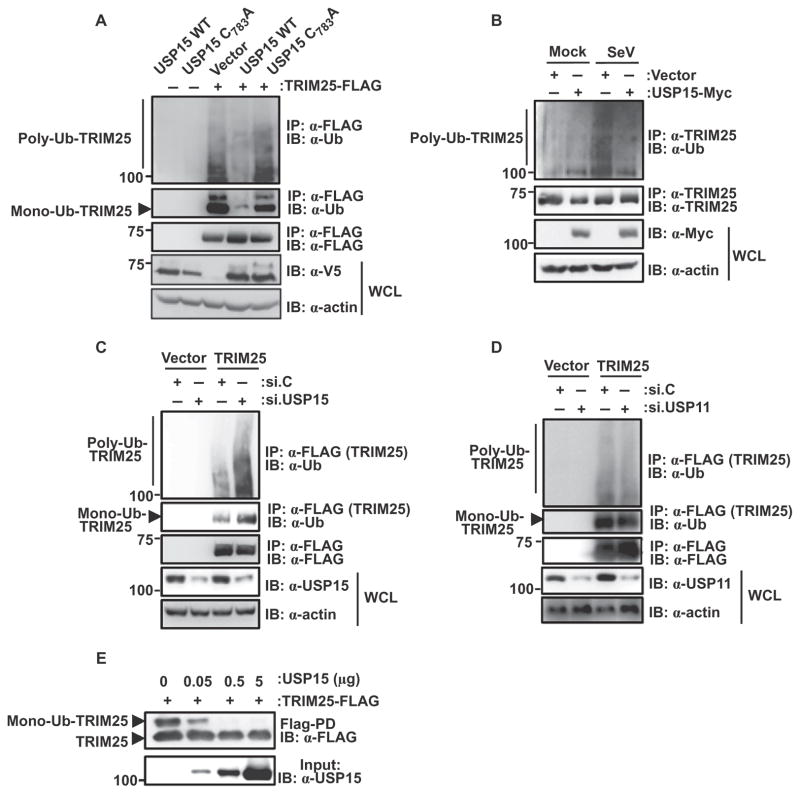
Fig. 2. USP15 deubiquitylates TRIM25.
(A) HEK 293T cells were transfected with empty plasmid or with plasmid encoding TRIM25-FLAG together with plasmids encoding V5-USP15 wild type (WT) or the V5-USP15 C783A mutant. Forty-eight hours later, WCLs were prepared and subjected to immunoprecipitation with α-FLAG antibody and Western blotting analysis with anti-ubiquitin (α-Ub) and α-FLAG antibodies. WCLs were further used for Western blotting with α-V5 and anti-actin (α-actin) antibodies. (B) HEK 293T cells were transfected with control plasmid or with plasmid encoding USP15-Myc. Thirty hours later, cells were mock-treated or were infected with SeV (50 HA U/ml) for 16 hours. Ubiquitylation of endogenous TRIM25 was determined by immunoprecipitation of samples with α-TRIM25 antibody followed by Western blotting analysis with α-Ub antibody. (C and D) HEK 293T cells were transfected with empty plasmid or plasmid encoding TRIM25-FLAG together with (C and D) nontargeting control siRNA (si.C), (C) USP15-specific siRNA (si.USP15), or (D) USP11-specific siRNA (si.USP11). Forty-eight hours later, WCLs were subjected to immunoprecipitation with α-FLAG and Western blotting analysis with α-Ub and α-FLAG. The extent of knockdown of USP15 or USP11 was determined by Western blotting analysis of WCLs with the appropriate antibodies. (E) An in vitro deubiquitylation assay was performed with TRIM25-FLAG and the indicated amounts of purified USP15 protein. Nonubiquitylated and monoubiquitylated forms of TRIM25 were detected by Western blotting analysis with α-FLAG. The input amounts of USP15 protein were determined by Western blotting analysis with α-USP15. Data in all panels are representative of three independent experiments.