Figure 2. Unchallenged microglia phagocytose apoptotic cells in the normal adult SGZ.
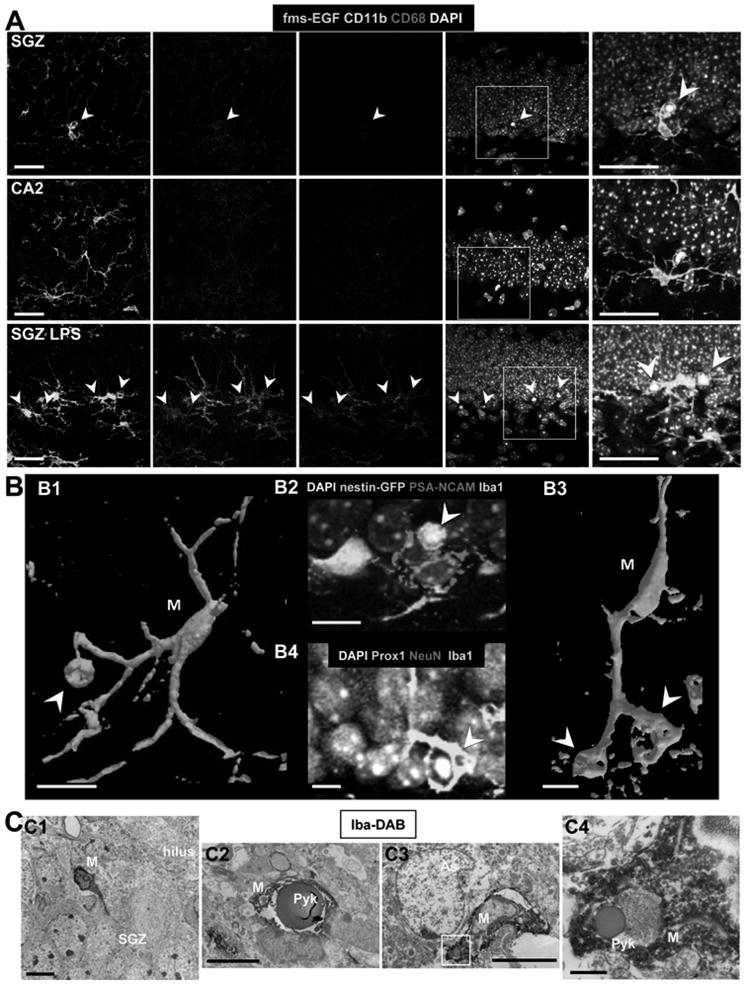
(A) Confocal photomicrographs of the expression of CD11b and CD68 in phagocytic microglia. Phagocytic SGZ and non-phagocytic CA2 microglia express low levels of CD11b and CD68, while LPS-challenged microglia express high levels of these markers (n=3 fms-EGFP mice; LPS 5mg/kg, 24h). The expression of fms-EGFP is similar in all experimental groups studied. Identical confocal settings were used to collect images from all animals. Enlarged insets of the merged images are shown at the end of each row. See also Fig. S2.
(B) Phagocytosis by microglia involves a ball-and-chain structure, formed by microglial en passant or terminal branches clearly distinguishable from the microglial cell body (M), as shown in volume rendering images of confocal z-stacks. The microglial phagocytic pouch in B1 (arrowhead) is shown in detail in B2: a pyknotic nucleus located on top of a PSA-NCAM+ NB and nearby nestin-GFP+ NPC is undergoing phagocytosis. The right microglial phagocytic pouch in B3 (arrowhead) is shown in detail in B4: a pyknotic nucleus located amongst immature and mature neurons (labeled with Prox1 and NeuN, respectively) is undergoing phagocytosis.
(C) Electron micrographs of the apoptotic cells and phagocytosis by microglia in the young adult SGZ. C1, Microglia (M), detected by Iba1-DAB immunostaining, is intermingled among the SGZ cells; C2, apoptotic cell (Pyk), identified by nuclear morphology, is engulfed by microglia (M); C3, terminal apoptotic debris is engulfed by microglia (M). C4, enlarged region of interest from C3.
Scale bars: A, 20μm (z=10μm); B, 10μm; C1-C3, 5μm; C4, 500nm. Arrowheads, phagocytic pouches; M, microglia; h, hilus; Pyk, pyknotic body; As, astrocyte.
