Figure 6.
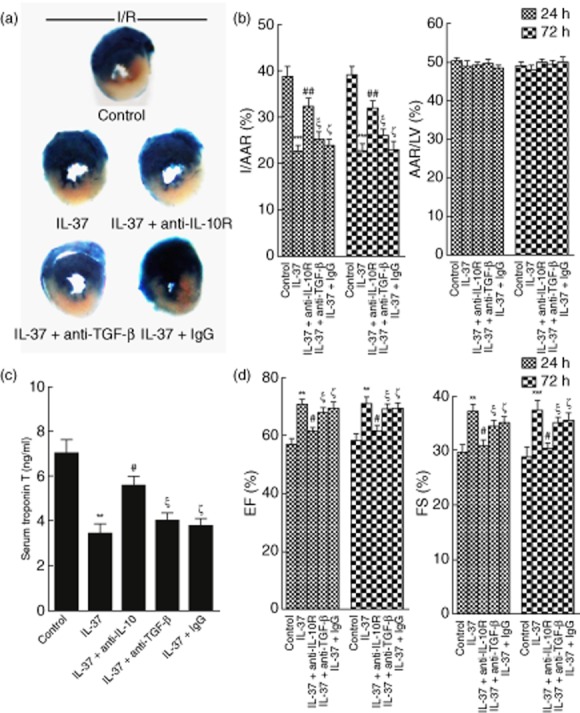
Interleukin (IL)-10 involved in the IL-37-mediated protective role in mice myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. IL-37-treated mice were concomitantly administered monoclonal antibody (mAb) against the IL-10 receptor (IL-10R), transforming growth factor (TGF)-β or isotype control [immunoglobulin (Ig)G], untreated I/R mice were used as a control. (a) Representative illustrations of infarct size after 24 h as stained by Evans Blue and triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC); the non-ischaemic area is indicated in blue, the area at risk (AAR) in red and the infarct area in white. (b) Quantification of infarct area/area at risk (I/AAR) and area at risk/left ventricular area (AAR/LV) 24 h and 72 h after reperfusion (n = 6). (c) Serum cardiac troponin T (cTnT) was measured in different groups 24 h after I/R (n = 6–8). (d) Ejection fraction (%EF) and fractional shortening (% FS) 24 h and 72 h after reperfusion (n = 6). **P < 0·01; ***P < 0·001 versus control. #P < 0·05; ##P < 0·01 versus IL-37-treated group. ξP > 0·05 versus IL-37-treated group. ζP > 0·05 versus IL-37-treated group.
