Figure 8.
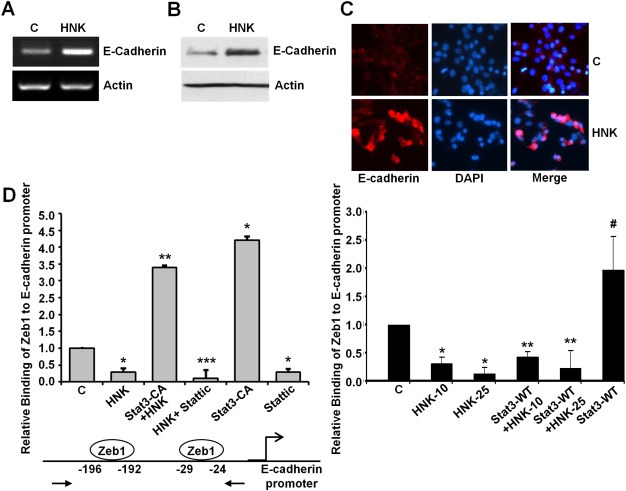
Honokiol increases E‐cadherin expression and inhibits the recruitment of Zeb1 on E‐cadherin promoter in a Stat3‐dependent manner. A, MCF7 cells were treated with vehicle (C) or 5 μM honokiol (HNK). Total RNA was isolated and examined for the expression of E‐cadherin using specific primers. B, MCF7 cells were treated as in A, total lysates were immunoblotted for E‐cadherin expression levels. C, MCF7 cells were treated as in A and subjected to immunofluorescence analysis of E‐cadherin. D, Soluble chromatin was prepared from MCF7 cells treated with vehicle (C), 5 μM honokiol (HNK), transfected with constitutively active Stat3 (Stat3‐CA) alone or in combination with honokiol (Stat3‐CA + HNK), 10 μM Stattic alone or in combination (HNK + Stattic) and subjected to chromatin immunoprecipitation assay using Zeb1 antibody. In another set, soluble chromatin was prepared from MCF7 cells treated with vehicle (C), 10 μM and 25 μM honokiol (HNK), transfected with wild‐type Stat3 (Stat3‐WT) alone or in combination with honokiol (Stat3‐WT + HNK‐10 and Stat3‐WT + HNK‐25) and subjected to chromatin immunoprecipitation assay using Zeb1 antibody. The purified DNA was analyzed by real‐time quantitative PCR using primers spanning the Zeb1‐binding sites at E‐cadherin promoter.
