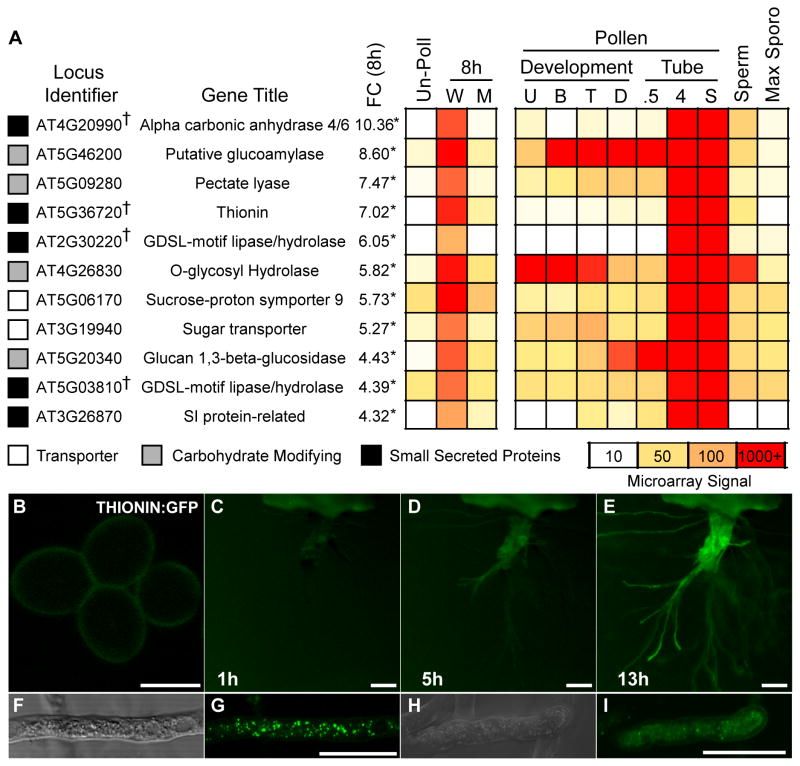
Figure 3. MYB97, MYB101, and MYB120 regulate gene expression during pollen pistil interactions.
(A) Expression heat map of genes identified as differentially expressed by microarray analysis. ms1 pistils were left un-pollinated (Un-Poll), or pollinated by either wild-type (W) or myb triple mutant (M) pollen and grown for 8 hours. The genes identified (Locus Identifier) are indicated with the gene name or predicted function (Gene Title). †, Array ID identifies two. The fold change (FC) between wild-type and myb triple mutant pollinations is shown, with asterisks (*) indicating fold changes that were statistically significant (P<0.05). Previously published data from pollen grain development [29], pollen tube growth [19], sperm cells [30], and sporophytic tissues [31] are included for comparison. Pollen development: U, Unicellular; B, Bicellular; T, Tricellular; D, Dry Pollen. Pollen tube: 0.5, 30′ in vitro grown pollen; 4, 4 hour in vitro grown pollen; S, Semi in vivo grown pollen tubes; Sperm, Isolated sperm cells, M - Max sporophytic expression from 7 tissue types.