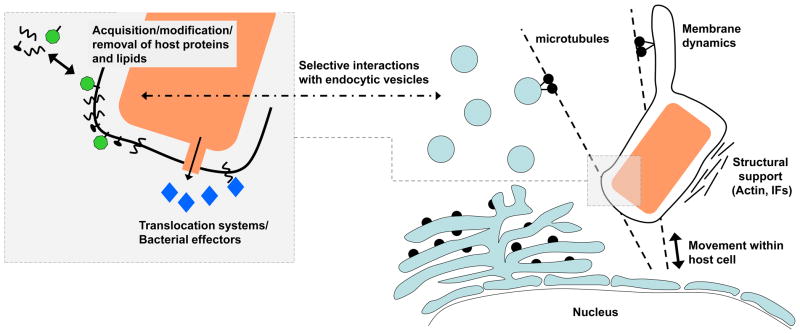
Fig 1. Maintenance of vacuole stability.
Vacuolar pathogens translocate effector proteins into the host cell to modify the vacuolar niche and subvert host cell pathways. Effectors direct the acquisition, modification and removal of host proteins and lipids of the vacuole membrane. Changes in lipid and protein composition alter the identity of the vacuole leading to selective interactions with endocytic vesicles. Interactions with the host cytoskeleton determine the subcellular localization of the vacuole, provide structural support and may facilitate vesicle recruitment. The dynamics of the vacuole membrane are affected by changes in the membrane lipids and interactions with microtubules and microtubule motors. Vacuole integrity is closely linked to vacuole biogenesis and subversion of these events frequently leads to vacuole rupture. In addition, the vacuole membrane may be compromised by the specialized secretion systems used to translocate effector proteins into the host cell.