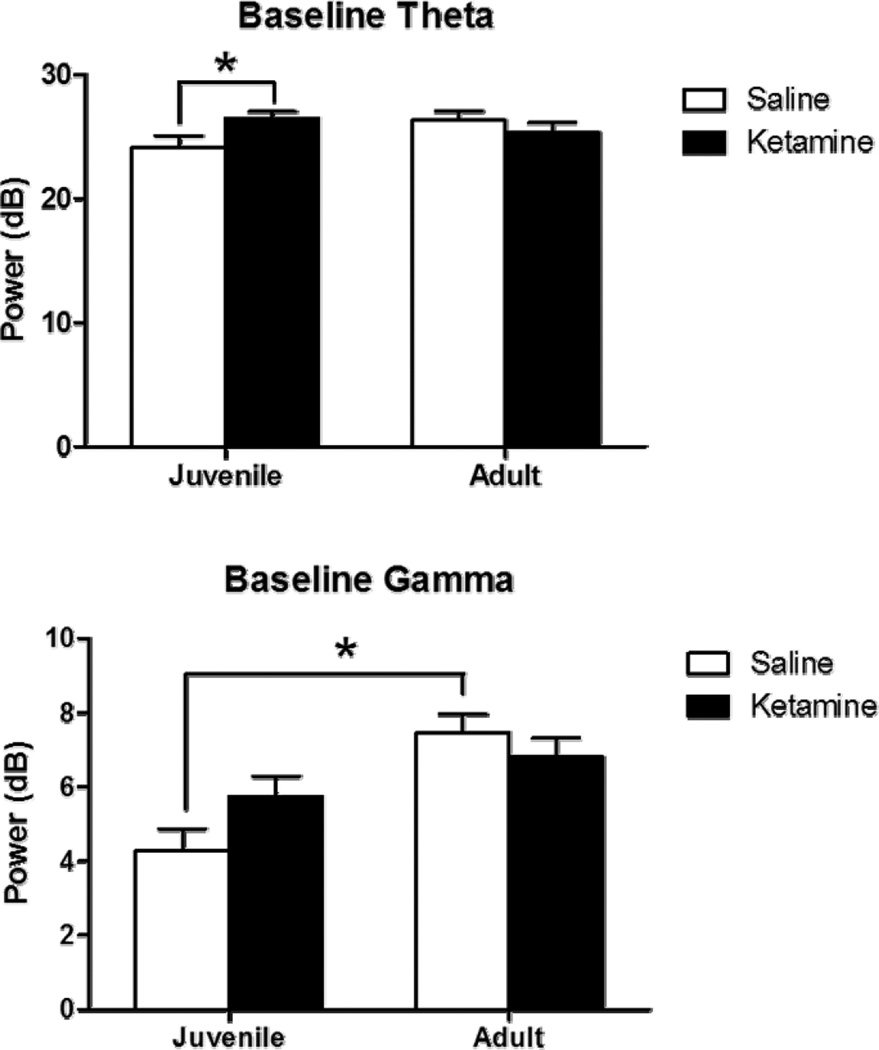
Figure 1.
Baseline EEG following juvenile saline (white) or ketamine (black) exposure assessed at 7 weeks (juvenile) and 12 weeks (adult). Figures 1A and B show theta (4 to 12 Hz) while figures 1C and D depict gamma (30 to 80 Hz). Gamma was quantified as the average of EEG power between 30 and 80 Hz, while theta was quantified as the average power between 4 and 12 Hz. Baseline theta power was increased in chronic ketamine-treated mice when assessed at the juvenile time-point, but this was not seen when assessed in adulthood. Saline-treated mice showed an age-related increase in gamma power as a function of increasing age (p<0.05) and this was not observed in ketamine-treated mice. Asterisk shows significance at p>0.05.