Abstract
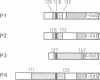
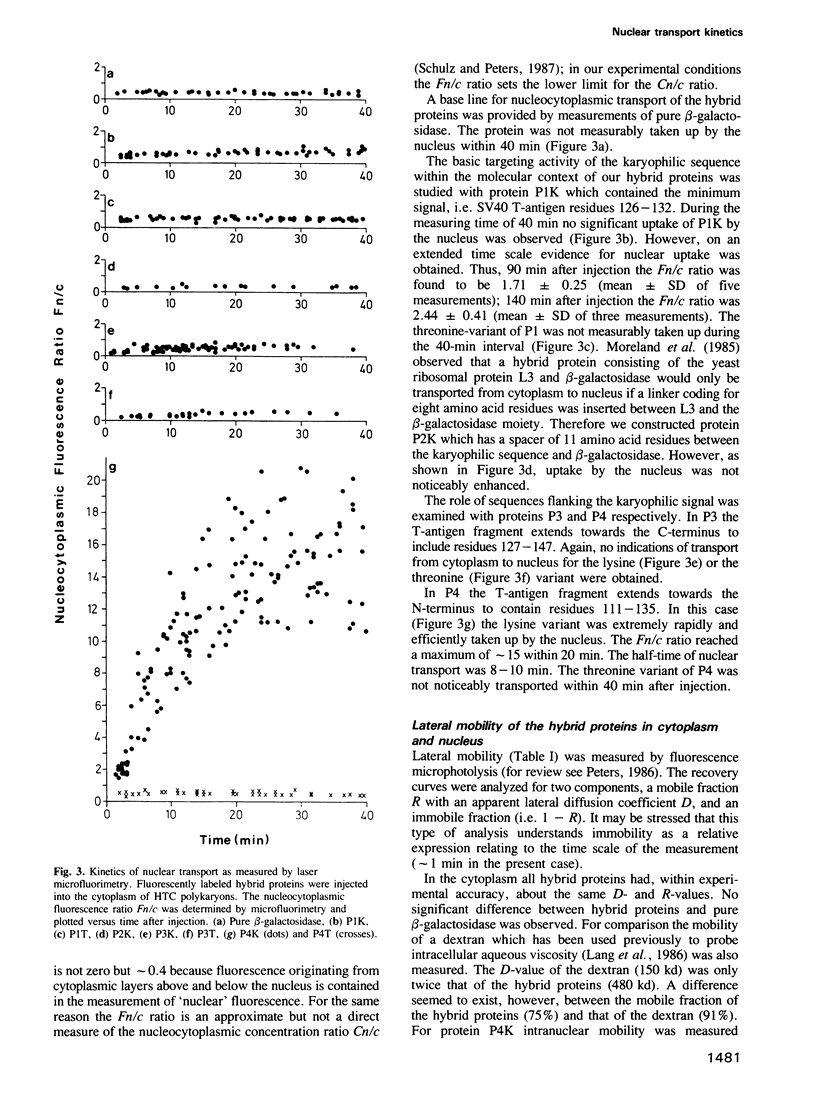
Selective nuclear protein transport was analyzed in single living cells. Hybrid proteins consisting of short stretches of the Simian virus 40 T-antigen and of the almost complete beta-galactosidase moiety were generated by molecular genetic methods and injected into the cytoplasm of rodent hepatoma cells. A histochemical assay showed that all proteins containing the karyophilic signal of the T-antigen (residues 126/127-132) were equally well accumulated by the nucleus within 15 h after injection. Microfluorimetric measurements of nuclear transport kinetics, however, revealed large differences. Proteins containing the karyophilic signal without flanking sequences were taken up by the nucleus on a time scale of hours. The same held for a protein containing T-antigen residues 127-147. However, a protein containing T-antigen residues 111-135 was accumulated by the nucleus with a half-time of 8-10 min reaching an equilibrium nucleocytoplasmic concentration ratio of greater than or equal to 15. Photobleaching measurements showed that, independently of subcellular localization, the mobility of all proteins was quite large. Thus, our measurements revealed a striking effect of T-antigen residues 111-125 on the kinetics of nuclear transport. Residues 111-125 do not seem to contain a second karyophilic signal. Conspicuously, however, they comprise a cluster of phosphorylation sites.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumann E. A., Hand R. Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation alter the structure of D2 hybrid T antigen. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):78–87. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.78-87.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürglin T. R., De Robertis E. M. The nuclear migration signal of Xenopus laevis nucleoplasmin. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2617–2625. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02552.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colledge W. H., Richardson W. D., Edge M. D., Smith A. E. Extensive mutagenesis of the nuclear location signal of simian virus 40 large-T antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4136–4139. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabauvalle M. C., Schulz B., Scheer U., Peters R. Inhibition of nuclear accumulation of karyophilic proteins in living cells by microinjection of the lectin wheat germ agglutinin. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Jan;174(1):291–296. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90163-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagert M., Ehrlich S. D. Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Robertis E. M., Longthorne R. F., Gurdon J. B. Intracellular migration of nuclear proteins in Xenopus oocytes. Nature. 1978 Mar 16;272(5650):254–256. doi: 10.1038/272254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Laskey R. A. Protein import into the cell nucleus. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:367–390. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Robbins J., Dilworth S. M., Roberts B., Richardson W. D. The nucleoplasmin nuclear location sequence is larger and more complex than that of SV-40 large T antigen. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):841–849. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson E. L., Reidler J. A. Analysis of cell surface interactions by measurements of lateral mobility. J Supramol Struct. 1979;12(4):481–489. doi: 10.1002/jss.400120408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning E., Nowak B., Burger C. Detection and characterization of multiple forms of simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):92–102. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.92-102.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerace L., Burke B. Functional organization of the nuclear envelope. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:335–374. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.002003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan D. S., Carroll R. B. Complex of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen and 48,000-dalton host tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):105–109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. N., Hereford L., Herskowitz I. Targeting of E. coli beta-galactosidase to the nucleus in yeast. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1057–1065. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz S. B., Fenichel I. R., Hoffman B., Kollmann G., Shapiro B. The intracellular transport and distribution of cysteamine phosphate derivatives. Biophys J. 1970 Oct;10(10):994–1010. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(70)86348-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis D. L., Lanford R. E., Butel J. S. Structural comparisons of wild-type and nuclear transport-defective simian virus 40 large tumor antigens. Virology. 1984 Apr 15;134(1):168–176. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90282-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Richardson W. D., Markham A. F., Smith A. E. Sequence requirements for nuclear location of simian virus 40 large-T antigen. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):33–38. doi: 10.1038/311033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Roberts B. L., Richardson W. D., Smith A. E. A short amino acid sequence able to specify nuclear location. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):499–509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90457-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Smith A. E. In vitro mutagenesis of a putative DNA binding domain of SV40 large-T. Virology. 1984 Nov;139(1):109–137. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90334-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krohne G., Franke W. W. Immunological identification and localization of the predominant nuclear protein of the amphibian oocyte nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1034–1038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kröger M., Hobom G. Restriction enzyme HgiCI characterization of the 6-nucleotide staggered cut sequence and its application in mismatch cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:3–10. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanford R. E., Butel J. S. Biochemical characterization of nuclear and cytoplasmic forms of SV40 tumor antigens encoded by parental and transport-detective mutant SV40-adenovirus 7 hybrid viruses. Virology. 1980 Sep;105(2):314–327. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanford R. E., Butel J. S. Construction and characterization of an SV40 mutant defective in nuclear transport of T antigen. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):801–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90415-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanford R. E., Kanda P., Kennedy R. C. Induction of nuclear transport with a synthetic peptide homologous to the SV40 T antigen transport signal. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):575–582. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90883-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang I., Scholz M., Peters R. Molecular mobility and nucleocytoplasmic flux in hepatoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;102(4):1183–1190. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.4.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr I. J., Stillman B., Gluzman Y. Regulation of SV40 DNA replication by phosphorylation of T antigen. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):153–160. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04733.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreland R. B., Nam H. G., Hereford L. M., Fried H. M. Identification of a nuclear localization signal of a yeast ribosomal protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6561–6565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J. W., Forbes D. J. The nucleus: structure, function, and dynamics. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:535–565. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paine P. L., Moore L. C., Horowitz S. B. Nuclear envelope permeability. Nature. 1975 Mar 13;254(5496):109–114. doi: 10.1038/254109a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters R. Fluorescence microphotolysis to measure nucleocytoplasmic transport and intracellular mobility. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Dec 22;864(3-4):305–359. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(86)90003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters R. Nucleo-cytoplasmic flux and intracellular mobility in single hepatocytes measured by fluorescence microphotolysis. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1831–1836. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02055.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanes J. R., Rubenstein J. L., Nicolas J. F. Use of a recombinant retrovirus to study post-implantation cell lineage in mouse embryos. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3133–3142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04620.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidtmann K. H., Hardung M., Echle B., Walter G. DNA-binding activity of simian virus 40 large T antigen correlates with a distinct phosphorylation state. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):1–12. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.1-12.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidtmann K. H., Schickedanz J., Walter G., Lanford R. E., Butel J. S. Differential phosphorylation of cytoplasmic and nuclear variants of simian virus 40 large T antigen encoded by simian virus 40-adenovirus 7 hybrid viruses. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):636–640. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.636-640.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz B., Peters R. Nucleocytoplasmic protein traffic in single mammalian cells studied by fluorescence microphotolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Oct 1;930(3):419–431. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90015-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira S. K., Chou J., Richaud F. V., Casadaban M. J. New versatile plasmid vectors for expression of hybrid proteins coded by a cloned gene fused to lacZ gene sequences encoding an enzymatically active carboxy-terminal portion of beta-galactosidase. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(1):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P. A., Keegan L. P., Ptashne M. Amino terminus of the yeast GAL4 gene product is sufficient for nuclear localization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5951–5955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. E., Kalderon D., Roberts B. L., Colledge W. H., Edge M., Gillett P., Markham A., Paucha E., Richardson W. D. The nuclear location signal. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 Oct 22;226(1242):43–58. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1985.0078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullmann A. One-step purification of hybrid proteins which have beta-galactosidase activity. Gene. 1984 Jul-Aug;29(1-2):27–31. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90162-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]