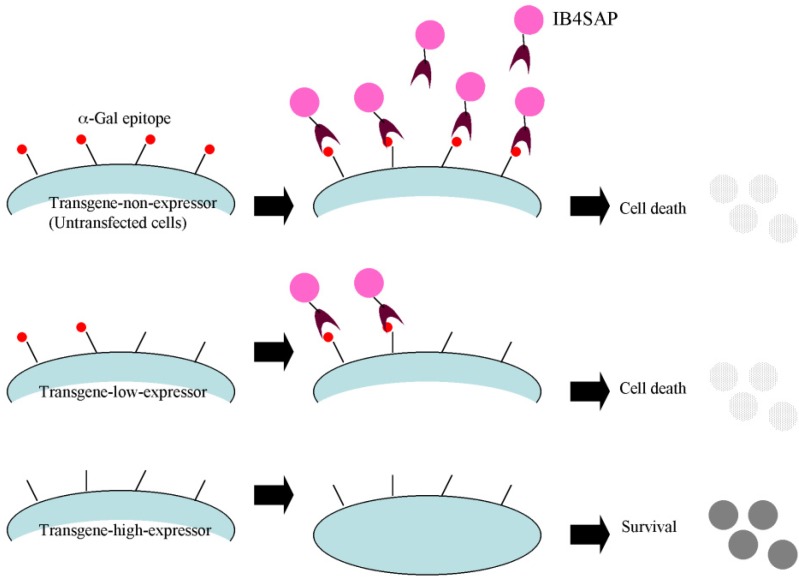
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of a mechanism for targeted toxin-mediated drug-free isolation of cells with high transgene expression. The untransfected cells (“transgene non-expressors”) expressing the α-Gal epitope on their surface are targeted by IB4SAP, which subsequently leads to cell death. When the cells are transfected with a vector expressing EndoGalC that digests the α-Gal epitope, the cells weakly expressing EndoGalC (“transgene low-expressors”) will still be killed by IB4SAP through binding to the residual α-Gal epitope on the cell surface. In contrast, the cells strongly expressing EndoGalC (“transgene high-expressors”) will survive IB4SAP treatment because of the complete loss of the α-Gal epitope on their surfaces.