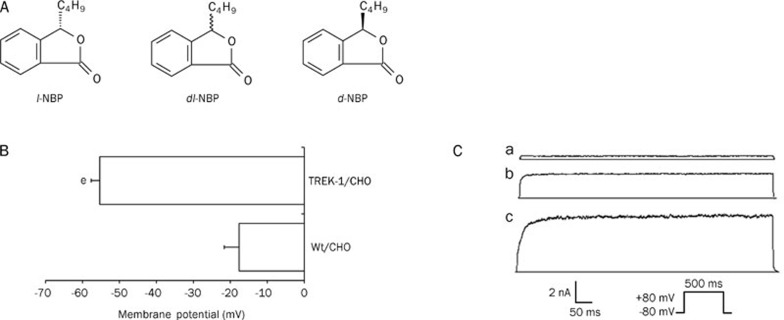
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of NBP and basic properties of the TREK-1 channel. (A) Chemical structures of racemic dl-NBP and its optical isomers. (B) The transfection of CHO cells with TREK-1 channels hyperpolarized the membrane potential, from -17.6±4.0 mV (Wt/CHO, n=7) to -55.3±2.4 mV (TREK-1/CHO, n=25). Values are expressed as the mean±SEM; eP<0.05 vs Wt/CHO cells. (C) Electrophysiological verification of the presence of TREK-1 channels in transfected CHO cells. a: Current elicited from Wt/CHO cells after being depolarized to +80 mV from a holding potential of -80 mV. b: Current elicited from TREK-1/CHO cells. c: Activation of TREK-1 currents by AA.