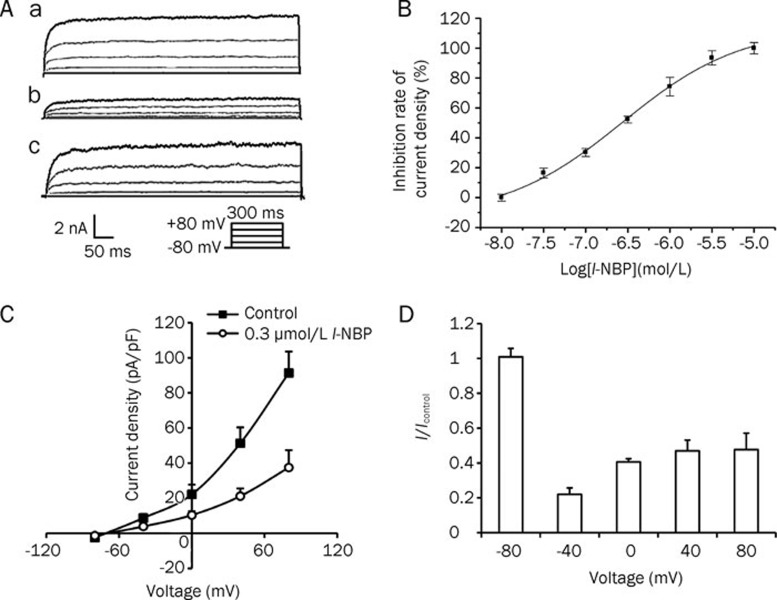
Figure 3.
l-NBP inhibited TREK-1 channel currents in a concentration-dependent manner. (A) The inhibition of TREK-1 currents by l-NBP. Representative current evoked by 300-ms voltage pulses from -80 mV to +80 mV in 40 mV increments. (a) Currents in TREK-1/CHO cells. (b) Inhibition of TREK-1 currents by 10 μmol/L l-NBP. (c) The TREK-1 currents returned to near the control level after washout. (B) Concentration-response curve for the inhibition of TREK-1 channels by l-NBP measured at +80 mV from the holding potential -80 mV at the end of a 300-ms pulse. Data are expressed as means±SEM from at least six cells. The IC50 was calculated as 0.06±0.03 μmol/L. (C) The I–V curve for the inhibition of TREK-1 channels by 0.3 μmol/L l-NBP was measured at +80 mV from the holding potential of -80 mV at the end of a 300-ms pulse. Data are expressed as means±SEM. (D) Voltage-independent inhibition of TREK-1 currents by l-NBP (10 μmol/L). Whole-cell current densities were normalized to control currents (lcontrol). The normalized current density for l-NBP-treated cells did not change significantly.