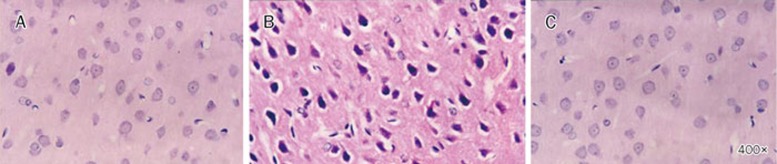
Figure 2.
Histological examination of neuronal damage. The photomicrograph of the hypothalamus for a normothermic rat (A), a heatstroke rats treated with vehicle solution (B), or a heatstroke rat treated with KYNA (C). Heatstroke rats were killed 85 min after the start of heat stress, whereas the normothermic rats were killed at the equivalent time period. The hypothalamus of the vehicle-treated rats showed cell body shrinkage, pyknosis of the nucleus, loss of Nissl substance, and disappearance of the nucleolus (B). However, heat-induced neuronal damage was reduced in group “C”. Magnification ×400