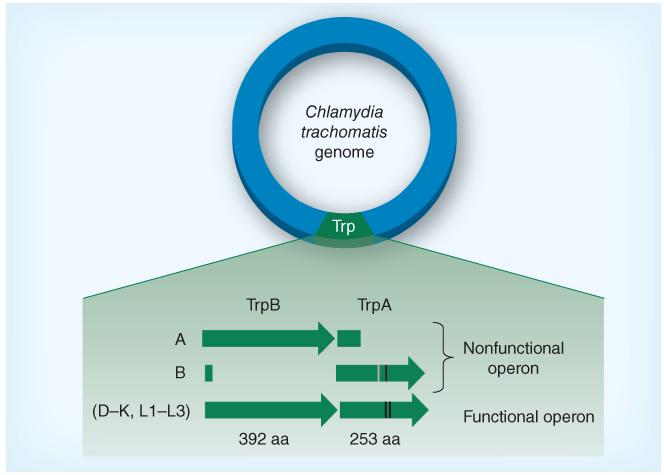
Figure 4. Trp synthase in different Chlamydia trachomatis serovars.
All ocular serovars sequenced thus far harbor a nonfunctional trpRBA operon, whereas trpRBA is functional for all sequenced genital serovars. For ocular serovars, mutations may result either in a truncated TrpA or in a nonsynonymous point mutation that results in incorporation of an amino acid that inhibits function. Point mutations have been described for serovars E, F, G and Ia for trpA (e.g., change at C177Y) and serovars L1–L3 (change at Q178E); however, these mutations do not impact TrpA function. Nonsynonymous point mutations are represented by black lines while deletion mutations and their effect on TrpA are represented by the gray line. Not drawn to scale.