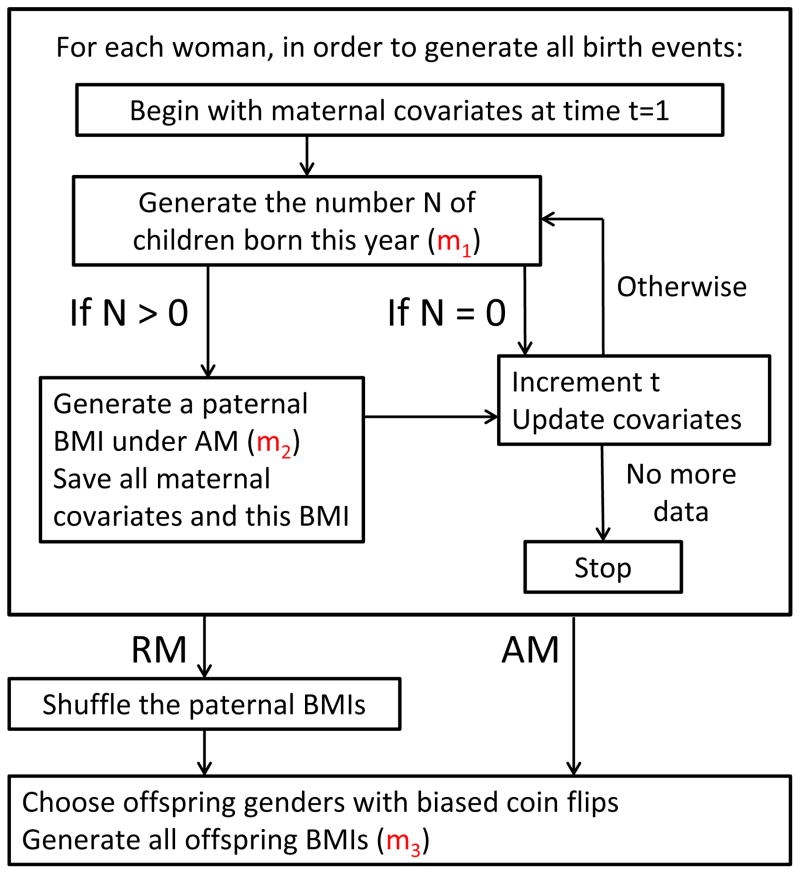
Figure 1.
A flow diagram for the operation of the Monte Carlo simulation framework. For a given woman, we generate some number N of offspring and, if any, a paternal BMI under assortative mating, for each year under consideration. We then move forward in time by one year and repeat until we have no more data for the woman under consideration. Once all birth events have been generated, offspring gender(s) and offspring BMI(s) are then simulated twice, once under these pairings (assortative mating present), and once where the paternal BMIs have been shuffled across birth events to enforce random mating.