Figure 1.
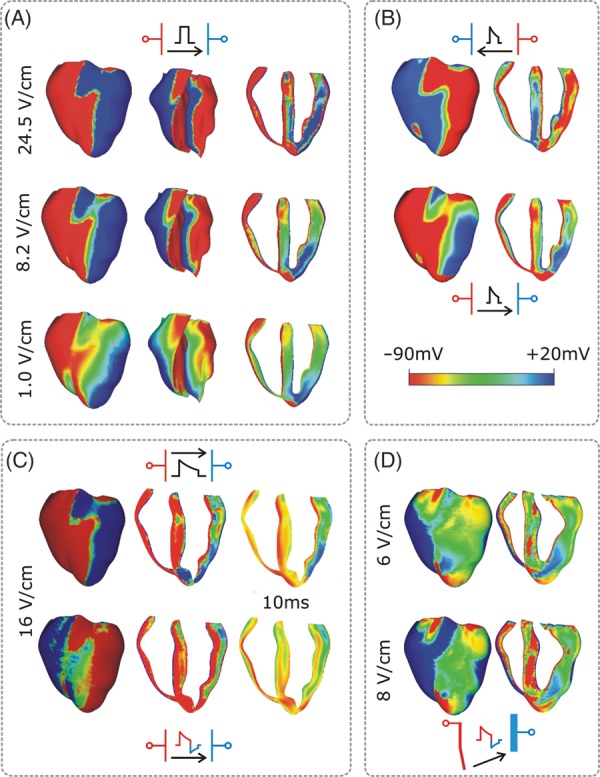
Transmembrane potential distribution at shock-end for various shock electrode configurations, waveforms, strengths, and polarities as indicated within each panel. The colour scale is saturated, i.e. Vm above 20 mV and below −90 mV appears as 20 and −90 mV, respectively. (A) External shocks are monophasic, 4 ms long, and of strengths shown in the figure; they are applied at a coupling interval of 105 ms. For each case, the anterior epicardium and endocardium, and a transmural view of the ventricles are shown. Images are based on figures published in Rodriguez and Trayanova.33 (B) External truncated-exponential monophasic shocks of reversed polarity and strength 5 V/cm. Anterior epicardium and transmural views of the ventricles are shown. Images are based on figures published in Rodriguez et al.2 (C) External truncated-exponential (62% tilt) monophasic and biphasic shocks are of 10 ms duration, coupling interval 220 ms, and of strengths shown in the figure. Anterior epicardium and transmural views of the ventricles are shown. Biphasic shock polarity reverses at 6 ms. In addition, the Vm distribution 10 ms after shock-end is shown in a transmural view. Images are based on figure published in Trayanova et al.15 (D) Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator-like electrode configuration delivers truncated-exponential (62% tilt) biphasic shocks of 10 ms duration at coupling interval 140 ms, and of strengths shown in the figure. Images are based on figure published in Trayanova et al.15
