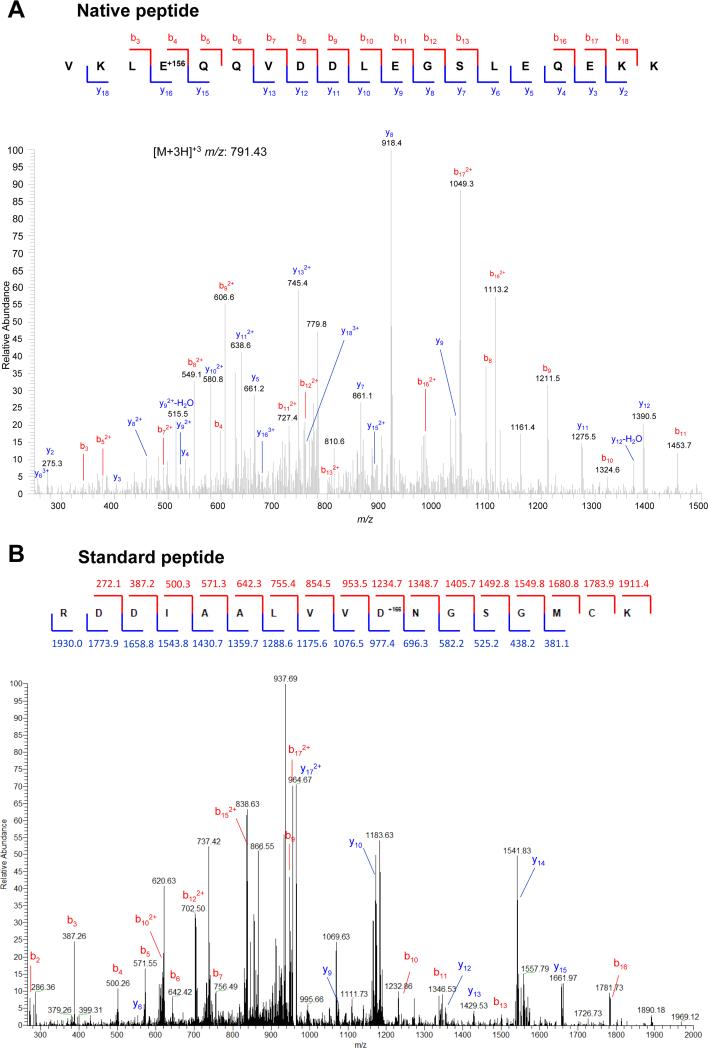
Figure 1. Arginylation on side chains of acidic residues in vivo (top) and in vitro (bottom).
Top, Mass spectrum of a naturally occurring arginylation on the side chain of Asp. Peptide sequence is indicated on top, with the arginylated residue marked by +156 (a mass of Arg). See Table 1 and Supplemental Table 1 for a full list of identified side-chain-arginylated proteins and Supplemental Table 2 for sequences and parameters of the identified peptides. Bottom, mass spectrum of a standard peptide, enzymatically arginylated on the side chain of Asp. Peptide sequence is indicated on top, with the arginylated residue marked by +166 (a mass of stable isotope labeled [13C,15N]-Arg used in the experiment). Numbers indicate the masses of b (red) and y (blue) ions.