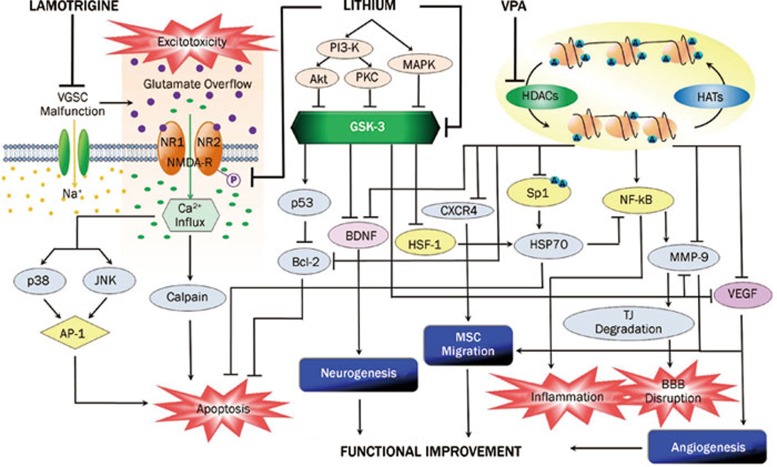
Figure 2.
An overview of the proposed signaling mechanisms underlying the protective effects of mood stabilizing drugs against experimental stroke. Lithium, VPA and lamotrigine inhibit glutamate excitotoxicity-induced neuronal apoptosis by different mechanisms. Lithium inhibits stroke-induced NMDA receptor overactivation by decreasing NR2 subunit tyrosine phosphorylation. This suppresses excitotoxicity-induced activation of either calpain or p38, JNK and subsequently AP-1 to block neuronal apoptosis. VPA suppresses glutamate excitotoxicity via regulation of gene expression, among other mechanisms. As a VGSC blocker, lamotrigine attenuates stroke-induced VGSC malfunction, prevents extracellular glutamate overflow, and consequently mitigates excitotoxicity and apoptosis. Lithium and VPA inhibit GSK-3 and HDACs, respectively, to transcriptionally regulate various downstream neuroprotective and neurotrophic factors, as well as to enhance mesenchymal stem cell migration. Bcl-2, an antiapoptotic factor, is upregulated by lithium and VPA under experimental stroke conditions. Expression of the neuroprotective molecule HSP70 is enhanced by lithium and VPA through HSF-1 and Sp1 activation, respectively. HSP70 is also proposed to exert anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting NF-κB activity. VPA attenuates BBB disruption by downregulating MMP-9 via NF-κB inhibition and preventing tight junction protein degradation shortly after ischemia. Long-term VPA treatment potentiates post-ischemic angiogenesis through upregulating VEGF and MMP-9 expression. Lithium also enhances VEGF and MMP-9 expression following long-term treatment. BDNF is activated by lithium and VPA, and the BDNF-TrkB signaling pathway is essential for enhancing post-ischemic neurogenesis and functional recovery. HAT: histone acetyltransferase; TJ: tight junctions; lines with solid arrows represent stimulatory effects; lines with flattened ends represent inhibitory effects; A: acetylated Lys residues of histone-tail proteins.