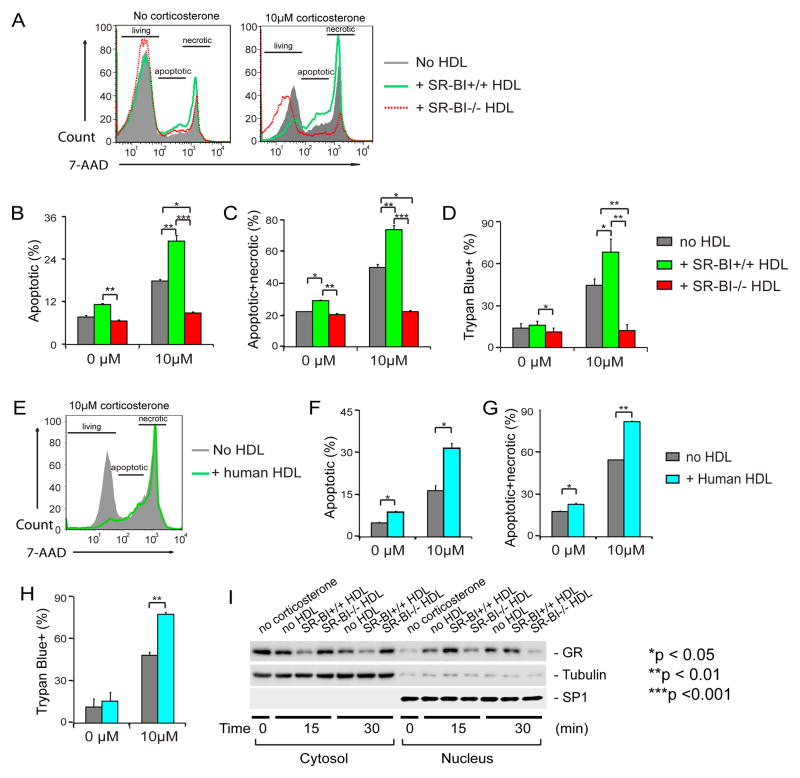
Figure 3. SR-BI+/+HDL enhances GC-induced thymocyte apoptosis through promoting GR translocation, but SR-BI−/− HDL lacks such regulatory activity.
A to D) SR-BI+/+ HDL enhances GC-induced thymocyte apoptosis, but SR-BI−/− HDL lacks such regulatory activity. Thymocytes harvested from wild-type mice were cultured in complete medium and incubated with/without 10 μM corticosterone in the presence/absence of HDL isolated from SR-BI+/+ (20% vol/vol, 0.345±0.011mg/mL by protein) or SR-BI−/− (20% vol/vol, 0.310±0.012 mg/mL by protein) for 18 h and analyzed with 7-AAD staining (A to C) and with Trypan Blue exclusion assays (D). n = 4 with duplicate measurements; Similar data were obtained when SR-BI−/− thymocytes were used (Supplemental Figure sV); E to H) Human HDL enhances GC-induced thymocyte apoptosis. Thymocytes were incubated with/without 10 μM of corticosterone in the presence/absence of human HDL (20% vol/vol, 0.168±0.012 mg/mL by protein) and analyzed with 7-AAD staining (E to G) and with Trypan Blue exclusion assays (H). n = 3 with triplicate measurements; I) SR-BI+/+HDL promoted GC-induced GR translocation but SR-BI−/− HDL lacked such regulatory activity. L929 cells were incubated with/without 100 nM Dex in the presence/absence of SR-BI+/+ or SR-BI−/− HDL for 15 and 30 min. The cytosol and nucleus fractions were isolated and the GR was detected with Western blot. Tubulin and SP1 were used as the markers of cytosol and nucleus, respectively.