Figure 6. Incorporation of free cholesterol into normal HDL impairs HDL’s regulatory activity on GC-induced thymocyte apoptosis.
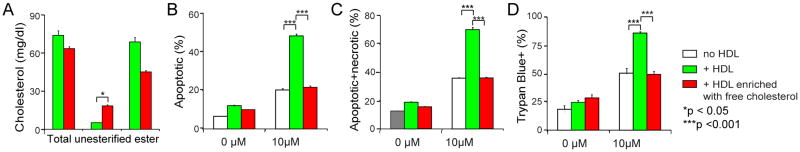
A) Incorporation of free cholesterol into normal HDL. Dipalmitory lecithin was sonicated with/without free cholesterol in saline, and then incubated with mouse serum for 24 h. HDL was isolated by ultracentrifugation and analyzed for cholesterol content. HDL treated with dipalmitory lecithin without free cholesterol addition was used as control HDL. n = 3 per group with duplicate measurements; B) to D). Incorporation of free cholesterol into normal HDL effects loss of HDL activity on GC-induced thymocyte apoptosis. Thymocytes from wild-type mice were cultured in complete medium and incubated with/without 10 μM corticosterone for 18 h in the presence/absence of HDL (20% vol/vol) enriched with free cholesterol (0.149±0.003 mg/mL by protein) or control HDL (0.119±0.010 mg/mL by protein). The cell death was analyzed by 7-AAD staining (B and C) and Trypan Blue assays (D). HDL treated with dipalmitory lecithin without free cholesterol addition was used as control HDL. n = 3 with duplicate measurements.
