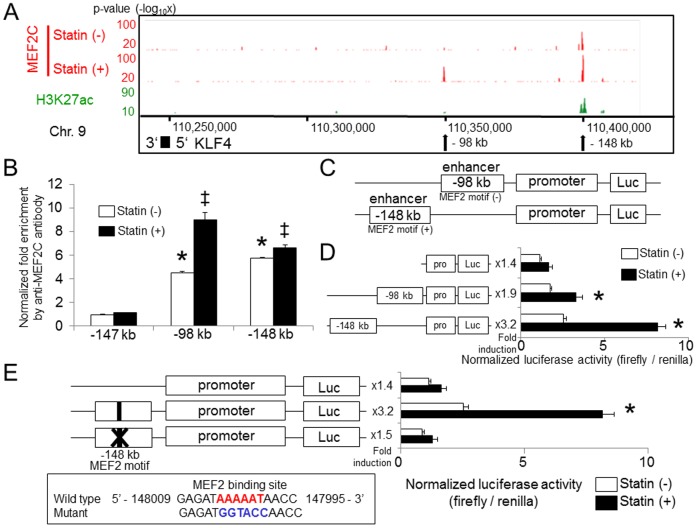
Figure 2. Binding of MEF2C at kb −148 from the TSS of the KLF4 gene is essential to pitavastatin-mediated KLF4 induction.
(A) HUVECs were incubated with 1 µM pitavastatin for 4 hours. As described in Methods, Chromatin immunoprecipitation was performed followed by deep sequencing. The localization and magnitude of MEF2C binding in the KLF4 transcription regulation region are illustrated. Two MEF2C binding sites in the KLF4 locus (−98 and −148 kb, relative to the TSS) were detected by ChIP-seq analysis. The localization of H3K27ac obtained by ChIP-seq is shown in the third lane. (B) Schematic structure of the transcriptional regulation region of the KLF4 gene. The sequences of the primers used are shown in Table S2D in File S1. (C) HUVECs were transiently transfected with a KLF4-luc, (−98 kb)-KLF4-luc and (−148 kb)-KLF4-luc plasmid together with the Renilla luciferase plasmid, and were treated with 1 µM pitavastatin for 12 hours. Luciferase activity was measured as described in the Methods section. Error bars indicate the S.D. (n = 3), *P<0.01 compared with pitavastatin (−), Student's t test. (D) HUVECs were transiently transfected with KLF4-luc, wild-type enhancer (−148 kb)-KLF4-luc and (enhancer −148 kb)-KLF4-luc containing a point mutation in the MEF2 binding element. Pitavastatin-mediated induction of promoter activity was abolished by mutation of the MEF2C binding site. Error bars indicate the S.D. (n = 3), *P<0.01 compared with pitavastatin (−), Student's t test. The Firefly luciferase activity value was normalized by Renilla luciferase activity.