Figure 2. Peripheral surgical wounding increases IL-6 levels in the mouse hippocampus.
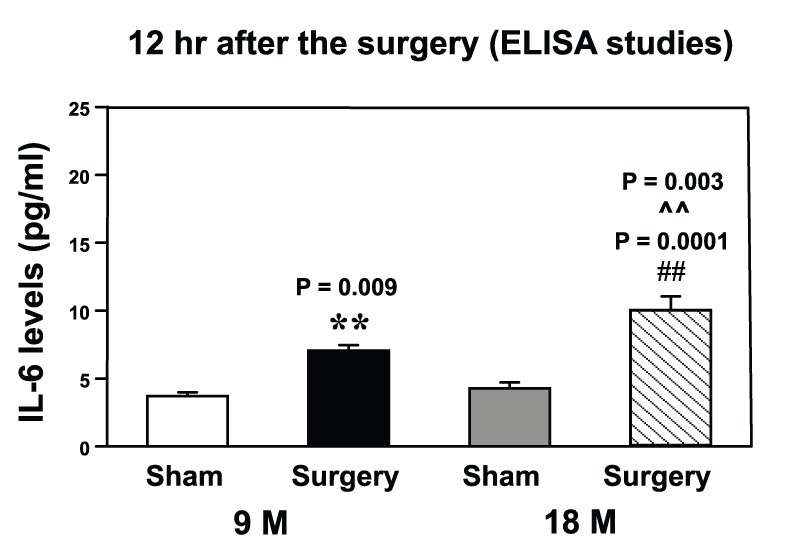
Peripheral surgical wounding increases the levels of IL-6 in the hippocampus of both 9 and 18 month-old mice at 12 hours after the peripheral surgical wounding. Age potentiates the peripheral surgical wounding-induced elevation of TNF-α levels. (** or ##: the difference between sham and peripheral surgical wounding; ∧∧: the interaction between the group and the treatment). IL, interleukin. N = 6.
