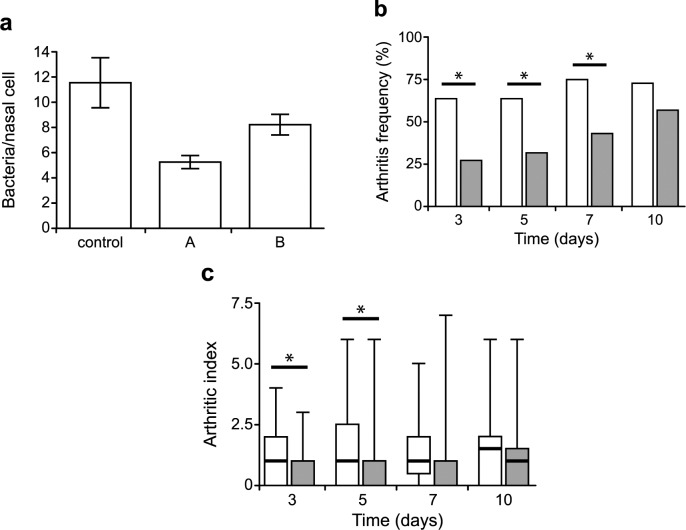
Figure 3.
Impact of C14-TOA 17 on adherence of S. aureus to desquamated human nasal epithelial cells and experimental infection. (a) Binding of S. aureus to squamous epithelial cells before or after treatment with 5-HE-C10-TMA 5 (A, 10 μM) or C14-TOA 17 (B, 1 μM). Counts represent the number of bacterial cells adhered to 100 nasal cells. Results are expressed as a mean of three experiments performed in duplicate. (b) Frequency of arthritis and (c) arthritic index of mice treated with 17 and challenged with S. aureus. White bars represent data from the control animals (PBS treated) and gray bars animals treated with 17 (10 mg/kg body weight). Data are presented as median (horizontal lines), interquartile ranges (bars), and ranges (error bars). An arthritic index was calculated by scoring all four limbs of each animal. Comparisons of groups for weight change and arthritis score were done by Mann–Whitney U test (∗, p < 0.05). Fischer exact probability test was used to calculate statistical differences in the frequency of arthritis.