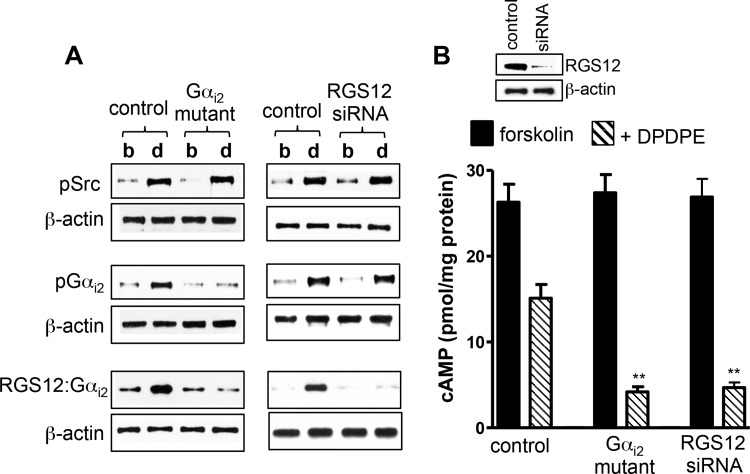
Fig. 4.
Expression of tyrosine-deficient Gαi2 mutant or RGS12 small interfering RNA (siRNA) blocks Gαi2-RGS12 association and enhances DPDPE-induced inhibition of cAMP. A: cultured smooth muscle cells transfected with control vector, vector containing Gαi2 mutant (Y69F, Y231F, or Y321F), or RGS12 siRNA were treated with 1 μM DPDPE for 1 min. Activation of cSrc (pSrc) was measured using specific phosphorylated (Tyr416) Src antibody. Gαi2 immunoprecipitates were used to measure tyrosine phosphorylation (pGαi2) using phosphotyrosine antibody and association of Gαi2 with RGS12 (RGS12-Gαi2) using RGS12 antibody. Immunoblots are representative of 4 separate experiments. b, Basal; d, DPDPE. Expression of Gαi2 mutant had no effect on cSrc activation, whereas suppression of RGS12 had no effect on cSrc activation and Gαi2 phosphorylation. B: cultured smooth muscle cells transfected with control vector, vector containing Gαi2 mutant (Y69F, Y231F, or Y321F), or RGS12 siRNA were pretreated with 10 μM forskolin for 10 min and then treated with 1 μM DPDPE for 1 min. cAMP levels were measured by radioimmunoassay. Basal levels (2.5 ± 0.25 to 2.7 ± 0.31 pmol/mg protein) of cAMP are similar in control cells and cells expressing Gαi2 mutant or RGS12 siRNA. Values (means ± SE of 5 experiments) are expressed as pmol/mg protein above basal level. **P < 0.01 compared with control.