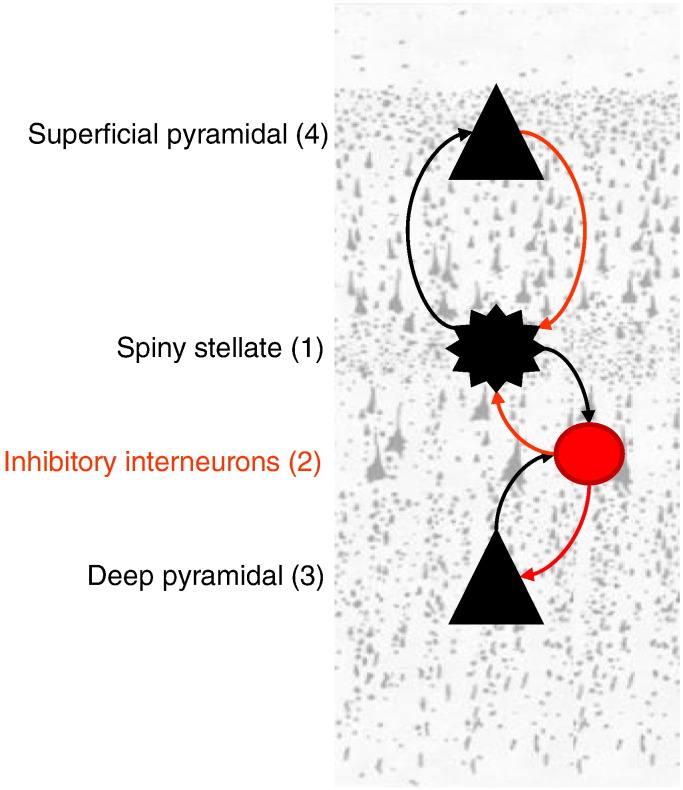
Fig. 2.
The canonical microcircuit (CMC) model. This model comprises four subpopulations and its development was motivated by theoretical considerations about hierarchical message passing and asymmetries of oscillation frequencies in the brain and its architecture is based upon intracellular recordings in cat visual cortex. This canonical microcircuit incorporates the neuronal sources of forward and backward connections in cortical hierarchies. These are the distinct superficial and deep pyramidal cell populations where superficial populations generate gamma responses whilst deep populations generate slower (alpha and beta) dynamics. The colours of the arrows correspond to excitatory (black) and inhibitory (red) connections respectively. The numbers in parentheses next to each cell-name serve as indices of the corresponding populations and their connections.