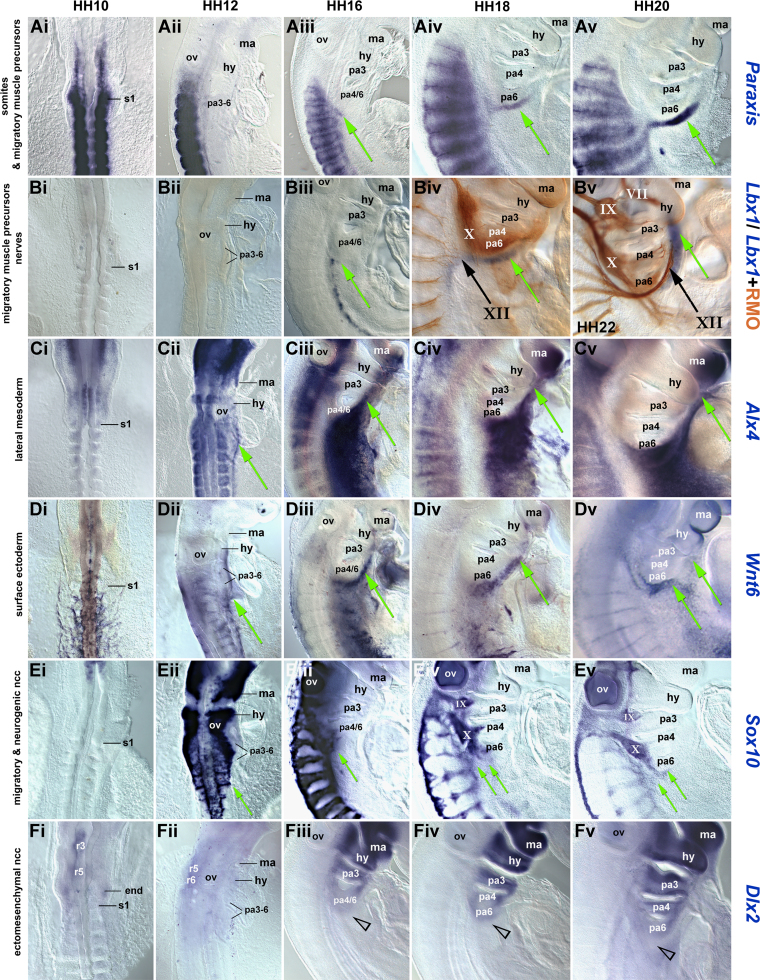
Fig. 1.
Coordinate rostral extension of marker gene expression domains at the chicken head–trunk interface. (Ai–Fi) dorsal, (Aii–Fii) dorsolateral and (Aiii–Fiii, Aiv–Fiv, Av–Fv) lateral views of the embryonic chicken head–trunk interface at the stages indicated at the top of the panel (Bv shows HH22), rostral to the top. The molecular markers are indicated on the right. Green arrows point at labelled cells using the circumpharyngeal route (black arrows for hypoglossal nerve). The expression domains of markers for the occipital lateral mesoderm (Alx4) and ectoderm (Wnt6) extend along the floor of the pharyngeal arches before this path is being used by the circumpharyngeal neural crest cells (Sox10 staining; Dlx2 labels the pharyngeal ectomesenchyme), the HMP (Paraxis, Lbx1 staining) and the hypoglossal nerve (RMO staining). Abbreviations: hy, hyoid arch; ma, mandibular arch; ncc, neural crest cells; ov, otic vesicle; pa3-6, pharyngeal arches 3-6; s1, 1st somite; VII, facial nerve; IX, glossopharyngeal nerve; X, vagal nerve; and XII, hypoglossal nerve.