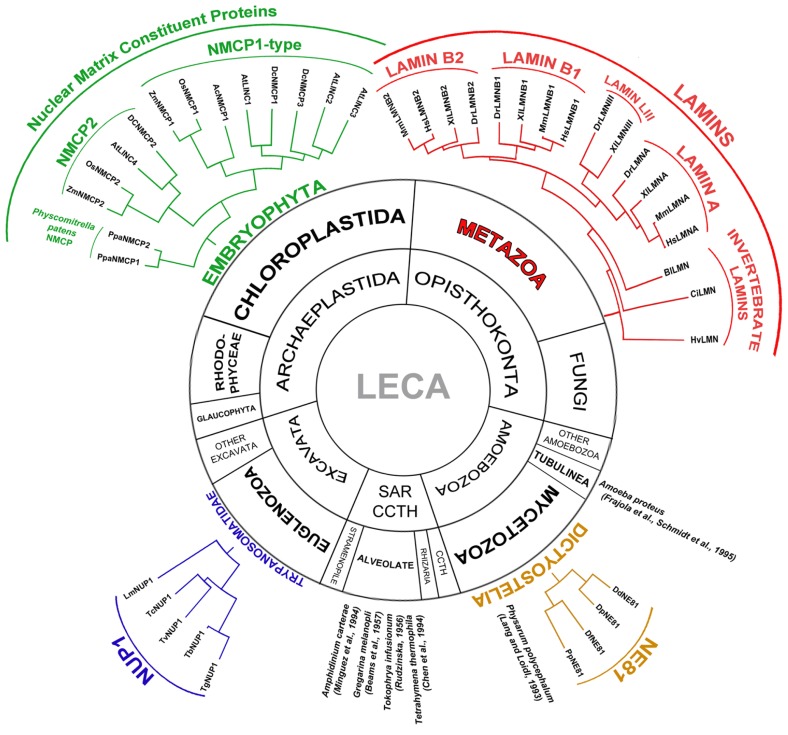
FIGURE 1.
Presence of the lamina in Eukaryota and classification and phylogenetic relationships between the lamina proteins in the different groups. The lamina has been described in different Eukaryotic groups: Metazoan, Embryophyta, Dictyostelia, Trypanosomatidae, Alveolate and Tubulinea, although its constituent proteins differ in different groups. The main components of the metazoan lamina are lamins. Most invertebrates express a single lamin while vertebrates contain four genes encoding lamin B1, lamin B2, lamin A, and lamin LIII (lost in mammals; Peter and Stick, 2012). In Dictyostelia the lamina is made up of nuclear envelope 81 (NE81) protein, which is considered an ancestor of lamins (Batsios et al., 2012; Kruger et al., 2012). The lamina was also reported in the nucleus of various Alveolate species: Amphidinium carterae, Gregarina melanopli, Tokophrya infusionum, Tetrahymena thermophila, and in Amoeba proteus (Tubulinea) and Physarum polycephalum (Dictyostelia) that do not contain a gene encoding the NE81 protein. The composition of the lamina in these species is not known. In Trypanosomatidae it is made up of a single nuclear periphery 1 (NUP1) protein (Rout and Field, 2001; Dubois et al., 2012). In Embryophyta the lamina is made up of nuclear matrix constituent proteins (NMCPs; Masuda et al., 1997; Ciska et al., 2013). NMCPs are classified in flowering plants into NMCP1-type proteins and NMCP2. Monocots have one NMCP1 and one NMCP2 proteins while dicots contain one NMCP2 and two or three NMCP1-type proteins. The moss Physcomitrella patens contains two NMCP proteins (Ciska et al., 2013). Selected species for the representation of the NMCP protein family: Allium cepa (Ac), Arabidopsis thaliana (At), Daucus carota (Dc), Oryza sativa (Os), Physcomitrella patens (Ppa), and Zea mays (Zm); NE81 proteins: Dictyostelium discoideum (Dd), Dictyostelium fasciculatum (Df), Dictyostelium purpureum (Dp), and Polysphondylium pallidum (Pp); NUP1 proteins: Trypanosoma brucei (Tb), Trypanosoma gambiense (Tg), Trypanosoma cruzi (Tc), Trypanosoma vivax (Tv), and Leishmania major (Lm); and lamins: Hydra vulgaris (Hv), Ciona intestinalis (Ci), Branchiostoma lanceolatum (Bl), Danio rerio (Dr), Xenopus laevis (Xl), Mus musculus (Mm), and Homo sapiens (Hs). LECA, the last eukaryotic common ancestor; SAR, stramenopile, alveolate, Rhizaria; CCTH, cryptomonads, centrohelids, telonemids, haptophytes.