FIG 1 .
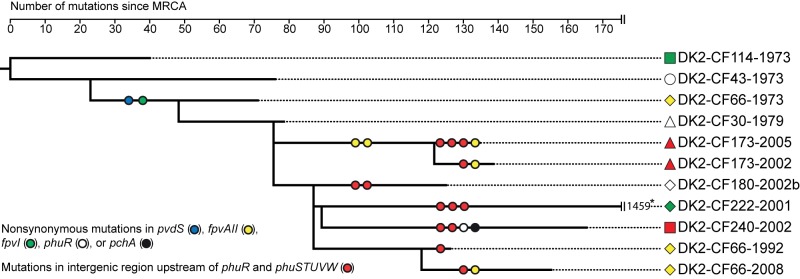
Maximum-parsimony phylogenetic tree showing the genetic relationship of the 11 DK2 clones included in this study. The phylogenetic tree is a subset of a phylogenetic tree from the work of Marvig et al. (2), who recently reported the genome sequences of 55 DK2 isolates. The shown tree depicts the genetic relationship of the 11 DK2 isolates included in this study, and it represents a total of 1,827 mutations (1,486 SNPs and 311 insertion/deletions) identified from whole-genome sequencing. Lengths of branches are proportional to the numbers of mutations except in the case of the truncated branch leading to isolate DK2-CF222-2001. For this hypermutator isolate, the large number of mutations is indicated at the end of the truncated branch. We searched the genomes for nonsynonymous mutations within genes encoding components of the pyoverdine, pyochelin, phu, has, feo, and fec iron acquisition systems (7, 11–13), and circles on the evolutionary branches denote that the specified gene is mutated in the branch. Due to the large number of mutations in the branch leading to the hypermutable isolate DK2-CF222-2001, only phuR and phuSTUVW intergenic mutations are specified. *, in addition to the three phuR and phuSTUVW intergenic mutations, this branch also contains nonsynonymous mutations in pvdS, pvdL, fpvI, the FpvAII gene, fpvR, phuR, fptA, pchH, pchG, pchF, pchE, and pchD (2).
