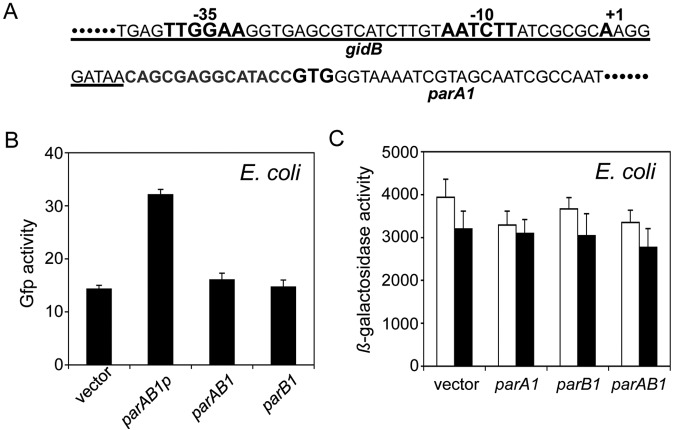
FIG 4 .
Regulation of parAB1 genes. (A) Sequence of parAB1 promoter region. The −35 and −10 promoter elements (bold letters) reside within the C-terminal region of the gidB gene (underlined). Also marked in bold are the transcription (+1) and translation (GTG) start sequences of parA1. (B) Promoter activities from cloned fragments carrying parAB1 genes and the adjoining upstream region (parAB1p) or parAB1 genes without the upstream region (parAB1) or the parB1 gene only (parB1). The activities were measured after fusing the fragments to gfp and measuring fluorescence intensities in E. coli cells exponentially growing in LB broth. The intensities are averages from three experiments. The high fluorescence from the gfp vector alone (the bar marked “vector”) is attributed to autofluorescence because the cells without the gfp vector gave similar fluorescence values. (C) Activity of parAB1 promoter fused to lacZ integrated into the E. coli chromosome using a λ vector. The lysogens contained either an empty vector (pBAD24) or the same vector carrying parA1, parB1, or parAB1 genes (pRN006, pRKG212, or pRN005, respectively). The lysogens were grown in LB broth with 0 (white bar) or 0.02% (black bar) arabinose.