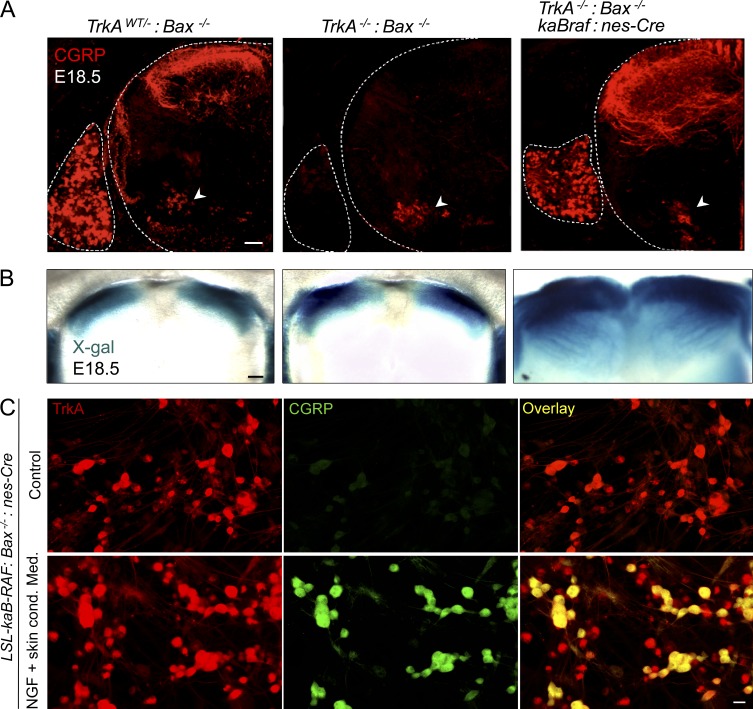
Figure 4.
Activation of B-RAF indirectly rescues CGRP expression in TrkA−/− nociceptive neurons. (A, left) Normal CGRP staining in the DRG and superficial dorsal horn. Arrowhead indicates CGRP-expressing spinal motoneurons. (middle) CGRP expression is completely abolished in the DRG and its projections in TrkA/Bax double-null mice. CGRP staining in spinal motoneurons is not affected by loss of TrkA signaling (arrowhead). (right) CGRP expression in DRG is rescued by expression of kaB-RAF, in the absence of TrkA signaling (LSL-kaBraf:nes-Cre:TrkA−/−:Bax−/−). Arrowhead indicates the CGRP+ motor neurons. Dashed white lines outline the spinal cord and DRG. (B) The nociceptive projection into the dorsal horn (left) does not depend on TrkA (middle). Expression of kaB-RAF causes overgrowth and ectopic targeting of these fibers (right). (A and B) Images are representative of three embryos each. (C) Activation of B-RAF does not directly induce CGRP expression in cultured DRG neurons. (top) No CGRP is expressed in 7-d in vitro cultures of dissociated E12.5 LSL-kaBraf:Bax−/−:nes-Cre DRG neurons. (bottom) NGF and conditioned medium from skin cultures are necessary to induce CGRP expression in E12.5 LSL-kaBraf:Bax−/−:nes-Cre DRG neurons. Images are representative of three independent experiments. This experiment has been repeated three times. Each experiment used two embryos per genotype. Bars: (A and B) 100 µm; (C) 20 µm.