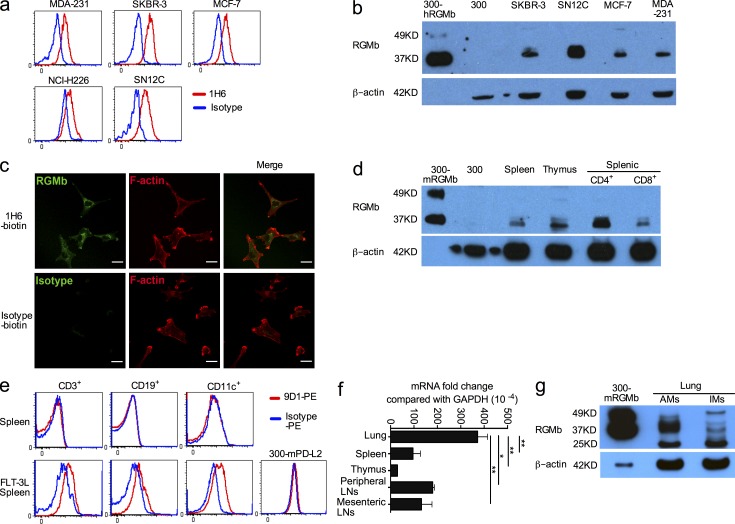
Figure 4.
RGMb can be expressed on the cell surface but is primarily localized intracellularly. (a) RGMb cell surface expression on human breast cancer cell lines (MDA-231, SKBR-3, and MCF-7), the nonsmall cell lung cancer cell line NCI-H226, and the renal cancer cell line SN12C was analyzed by flow cytometry with mAb 1H6 (red) or isotype control (blue). (b) RGMb expression by Western blotting using mAb 1H6. The loading amount was 60–80 µg/lane except for 0.5 µg/lane for 300-hRGMb. (c) SKBR-3 cells were stained for RGMb (1H6-biotin) or isotype control plus streptavidin-Alexa Fluor 488 (green), and then with Phalloidin-TRIC to label F-actin, and analyzed by confocal microscopy. Bars, 25 µm. (d) RGMb expression by Western blotting using mAb 1H6. The loading amount was 60–80 µg/lane, except for 0.5 µg/lane for 300-mRGMb cells. (e) Splenocytes from naive mice and mice treated with FLT-3L as well as 300-mPD-L2 cells (negative control) were stained for surface markers CD3, CD19, and CD11c. Then intracellular flow cytometry staining with PE-conjugated RGMb mAb 9D1 (red) or rat IgG2a (blue) was used to analyze RGMb expression in these cells. (f) RGMb expression in unstimulated cells from the indicated mouse organs by qRT-PCR. Data are mean ± SEM; n = 2; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. Ordinary one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test. (g) RGMb expression in lung AM and IM by Western blotting as in d. All data are representative of two or more experiments.