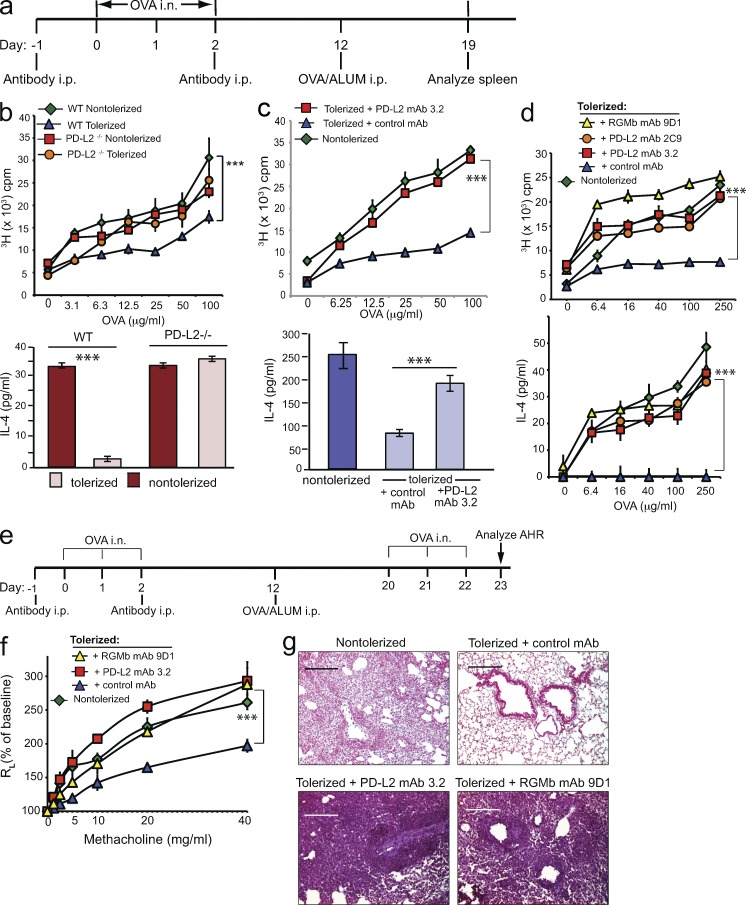
Figure 6.
PD-L2 or RGMb blockade inhibits induction of respiratory tolerance. (a) Experimental protocol for induction of respiratory tolerance. (b–d) PD-L2–deficient or WT mice in b, and WT mice injected with the indicated mAb in c and d, were exposed to OVA i.n. (tolerized) or PBS (nontolerized) and subsequently received 50 µg OVA/ALUM i.p. T cell proliferation (top) and IL-4 production (bottom) in response to restimulation with OVA in vitro are shown. n = 2–3. Data are representative of two to five experiments. Data are mean ± SEM, *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.005. (b, top) two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. (c, top, and d) Two-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test. (b and c, bottom) Two-tailed Student’s t test. (e) Experimental protocol used in f and g. (f) WT mice injected with the indicated mAb were exposed to OVA i.n. or PBS, immunized with 50 µg OVA/ALUM i.p. Mice were subsequently challenged with OVA i.n. on three consecutive days and assessed for AHR by measuring lung resistance (RL) and dynamic compliance (Cdyn). Data are the mean ± SEM of 4 mice/group. (g) Lung histopathology of mice from panel f. Lung tissue was stained with H&E and analyzed for cell infiltration. Data in f and g are representative of two experiments.