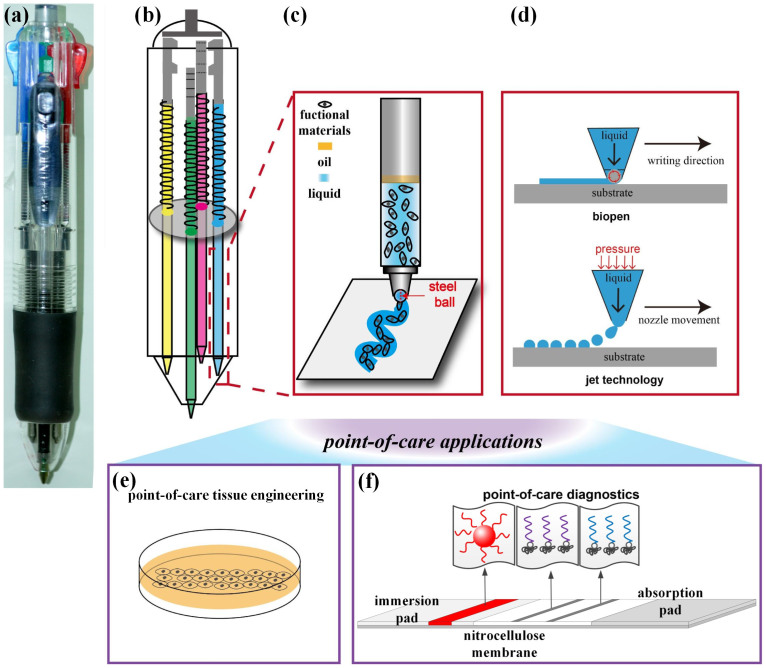
Figure 1. Schematic of BioPen structure, working principle, and point-of-care applications.
(a) BioPen is constructed by replacing the ink of a commercial ballpoint pen and optimizing conditions for writing specific functional “inks”. (b) One BioPen can house multiple functional cartridges. (c) The suspension of functional materials can be patterned onto a range of substrates by simply writing at a prescribed speed. (d) One advantage of BioPen over inkjet technology is that it lays down continuous rather than discrete streams of ink, enabling superior connectivity. (e)(f) Additional advantages are portability and accuracy, enabling applications including point-of-care tissue engineering and point-of-care diagnostics.