FIG 5.
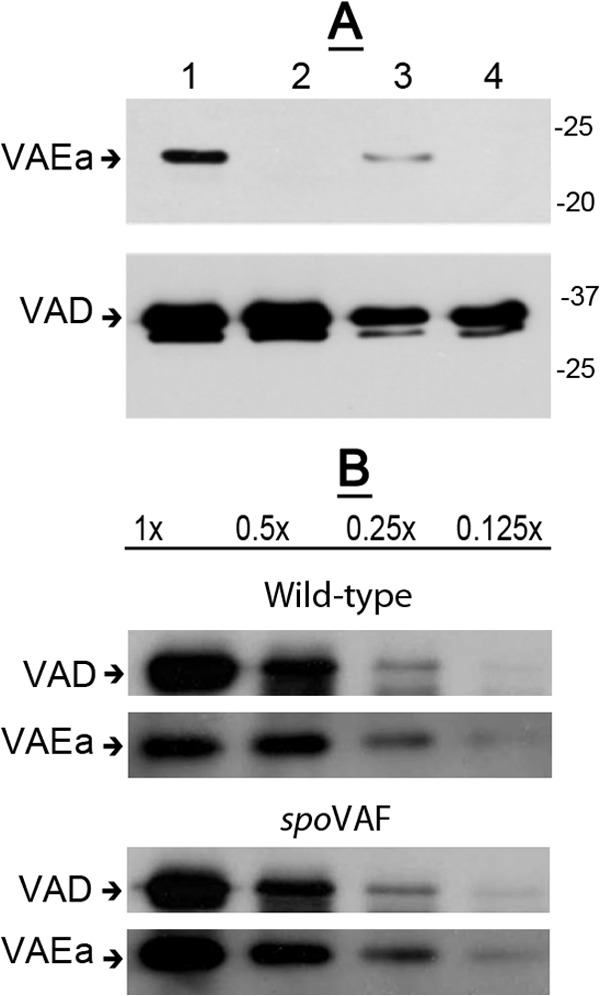
(A, B) Levels of SpoVAD and SpoVAEa in lysates of wild-type and spoVAEa and spoVAF mutant spores. Spores of B. subtilis strains PS533 (wild type) (A, B), PS4348 (spoVAEa mutant) (A), and PS4351 (spoVAF mutant) (B) were decoated, and lysates were prepared as described in Materials and Methods. Various amounts of protein in the lysates from the spores of the two strains (∼5 × 107 spores for analysis of SpoVAEa or ∼5 × 106 spores [each defined as 1×] for analysis of SpoVAD) were analyzed by Western blotting with antiserum against either SpoVAEa or SpoVAD as described in Materials and Methods. The lanes in panel A are as follows: 1, 1× protein from wild-type spores; 2, 1× protein from spoVAEa mutant spores; 3, 0.25× protein from wild-type spores; 4, 0.25× protein from spoVAEa mutant spores. The arrows labeled VAEa and VAD on the left of the panels denote the migration positions of SpoVAEa and SpoVAD, respectively, and the values to the right of panel A are the masses of molecular size marker proteins in kilodaltons.
