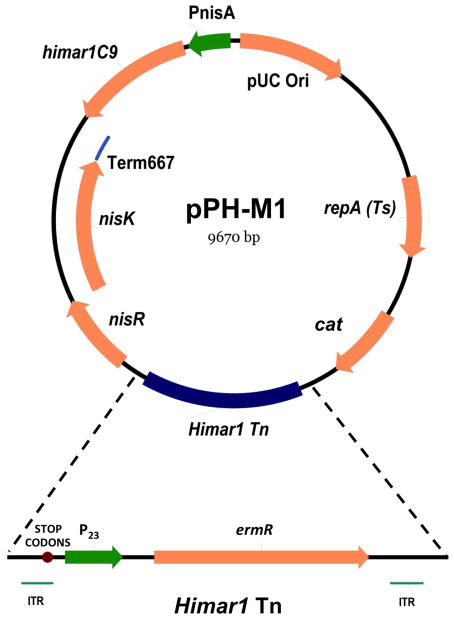
Fig. 1. The Himar 1 transposase/transposon delivery vector, pPH-M1, generated for Himar1 Tn mutagenesis in L. reuteri.
Genes for the Himar1 transposase, selective antibiotic resistance cassettes, nisin-inducible expression system and elements important for transposition were all combined into a single, conditionally replicative vector for use in L. reuteri. Conditional replication is temperature-dependent, and an increase in temperature to 45°C results in plasmid elimination. cat, chloramphenicol resistance gene; ermR, erythromycin resistance gene; ITR, inverted terminal repeats (ITRs) recognized by the Himar1 transposase; STOP CODONS, translational stop codons; P23, constitutive P23 promoter; nisR and nisK, two-component regulatory elements required for nisin-induced expression system; Term 667, translational stop codons; himar1C9, hyperactive mutant of Himar1 transposase; PnisA, promoter for nisin-induced expression system; pUC Ori, origin of replication for E. coli; repA(Ts), gene encoding temperature sensitive mutant of replication factor RepA, required for replication in L. reuteri